Macro View Rotation
| Description |
|---|
| This GUI allows the view to be rotated with more precision than when using the mouse. Rotation is according to axes fixed with respect to the user and not the objects, though the aim is that the objects rotate about their approximate shared centre rather than the view centre. The GUI defaults to the top right of the screen, this behaviour can be changed by editing. |
| Author |
| Joe Dowsett |
| Download |
| ToolBar Icon |
| Links |
| Macros recipes How to install macros How to customize toolbars |
| Macro Version |
| 1.0 |
| Date last modified |
| 2012-01-04 |
| FreeCAD Version(s) |
| All |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| See also |
| Macro Rotate View, Macro FCCamera |
Description
This GUI allows the view to be rotated with more precision than when using the mouse. Rotation is according to axes fixed with respect to the user and not the objects, though the aim is that the objects rotate about their approximate shared centre rather than the view centre.
The GUI defaults to the top right of the screen, this behaviour can be changed by editing.
Temporary code for external macro link. Do not use this code. This code is used exclusively by Addon Manager. Link for optional manual installation: Macro
# This code is copied instead of the original macro code
# to guide the user to the online download page.
# Use it if the code of the macro is larger than 64 KB and cannot be included in the wiki
# or if the RAW code URL is somewhere else in the wiki.
from PySide import QtGui, QtCore
diag = QtGui.QMessageBox(QtGui.QMessageBox.Information,
"Information",
"This macro must be downloaded from this link\n"
"\n"
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD-macros/master/PureGui/ViewRotation.FCMacro" + "\n"
"\n"
"Quit this window to access the download page")
diag.setWindowFlags(QtCore.Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
diag.setWindowModality(QtCore.Qt.ApplicationModal)
diag.exec_()
import webbrowser
webbrowser.open("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD-macros/master/PureGui/ViewRotation.FCMacro")
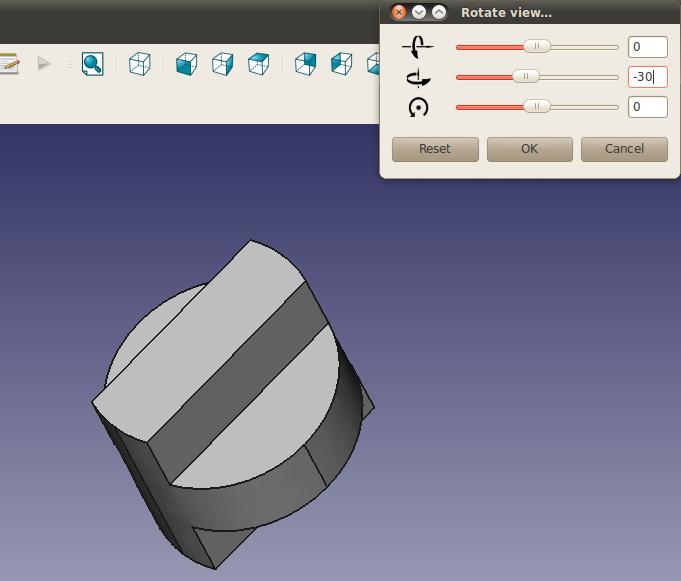
Three icons are referred to symbolise the rotation directions. A zip file containing these icons can be found here, the images should be placed in the folder containing your macros. Please feel free to contribute better ones!
Script
The latest version of the macro is to be found at ViewRotation.FCMacro but the easiest way to install this macro is through the Addon Manager.
Macro View Rotation.FCMacro
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#
# FreeCAD macro ViewRotation.
# This GUI allows the view to be rotated with more precision than when using
# the mouse. Rotation is according to axes fixed with respect to the user and
# not the objects, though the aim is that the objects rotate about their
# approximate shared centre rather than the view centre.
# The GUI defaults to the top right of the screen, this behaviour can be
# changed by editing.
# [https://forum.freecad.org/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=1784&hilit=View+Rotation#p12012 View+Rotation]
from __future__ import division
__Name__ = 'View Rotation'
__Comment__ = 'This GUI allows the view to be rotated precisely'
__Author__ = 'Joe Dowsett'
__Version__ = '1.0'
__License__ = 'CC-BY-3.0'
__Web__ = 'https://wiki.freecad.org/Macro_View_Rotation'
__Wiki__ = 'https://wiki.freecad.org/Macro_View_Rotation'
__Icon__ = ''
__Help__ = 'Rotation is according to axes fixed with respect to the user.'
__Status__ = ''
__Requires__ = ''
__Files__ = 'ViewRotationOut.png,ViewRotationRight.png,ViewRotationUp.png'
from math import pi
import os
from PySide import QtCore
from PySide import QtGui
from pivy import coin
import FreeCAD as app
import FreeCADGui as gui
def get_macro_dir():
"""Return the directory where macros are located"""
default_macro_dir = os.path.join(app.ConfigGet('UserAppData'), 'Macro')
return app.ParamGet('User parameter:BaseApp/Preferences/Macro').GetString('MacroPath', default_macro_dir)
def find_centre():
doc = app.activeDocument()
if doc is None:
return app.Vector(0, 0, 0)
xmax = 0
xmin = 0
ymax = 0
ymin = 0
zmax = 0
zmin = 0
for obj in doc.Objects:
try:
if obj.TypeId[:4] == 'Mesh':
box = obj.Mesh.BoundBox
elif obj.TypeId[:6] == 'Points':
box = obj.Points.BoundBox
elif obj.TypeId[:4] == 'Part':
box = obj.Shape.BoundBox
else:
continue
except AttributeError:
continue
xmax = max(xmax, box.XMax)
xmin = min(xmin, box.XMin)
ymax = max(ymax, box.YMax)
ymin = min(ymin, box.YMin)
zmax = max(zmax, box.ZMax)
zmin = min(zmin, box.ZMin)
return app.Vector((xmax + xmin) / 2, (ymax + ymin) / 2, (zmax + zmin) / 2)
class RotateGui(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(RotateGui, self).__init__()
self.init_ui()
self.init_rotate()
def init_ui(self):
macro_dir = get_macro_dir()
self.sliders = []
self.line_edits = []
vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout()
icons = ('ViewRotationRight.png', 'ViewRotationUp.png', 'ViewRotationOut.png')
for icon in icons:
slider = QtGui.QSlider(QtCore.Qt.Horizontal, self)
slider.setFocusPolicy(QtCore.Qt.NoFocus)
slider.setSingleStep(5)
slider.setPageStep(15)
slider.setValue(0)
slider.setMaximum(180)
slider.setMinimum(-180)
slider.valueChanged[int].connect(self.valueChange)
self.sliders.append(slider)
line_edit = QtGui.QLineEdit(self)
line_edit.setText('0')
line_edit.setAlignment(QtCore.Qt.AlignRight)
line_edit.returnPressed.connect(self.valueEntered)
self.line_edits.append(line_edit)
label = QtGui.QLabel(self)
label.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap(os.path.join(macro_dir, icon)))
hbox = QtGui.QHBoxLayout()
hbox.addWidget(label, 1, QtCore.Qt.AlignCenter)
hbox.addWidget(slider, 4)
hbox.addWidget(line_edit, 1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox)
reset_button = QtGui.QPushButton('Reset')
reset_button.clicked.connect(self.reset)
ok_button = QtGui.QPushButton('OK')
ok_button.clicked.connect(self.close)
cancel_button = QtGui.QPushButton('Cancel')
cancel_button.clicked.connect(self.cancel)
hbox = QtGui.QHBoxLayout()
hbox.addWidget(reset_button, 1)
hbox.addWidget(ok_button, 1)
hbox.addWidget(cancel_button, 1)
vbox.addStretch(1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox)
self.setLayout(vbox)
desktop_widget = QtGui.QDesktopWidget()
right = desktop_widget.availableGeometry().width()
self.setGeometry(right - 300, 0, 300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Rotate view')
self.show()
def init_rotate(self):
self.internal = False
self.current = 0
self.cam = gui.activeDocument().ActiveView.getCameraNode()
self.centre = coin.SbVec3f(find_centre())
self.view = self.cam.orientation.getValue()
self.pos = self.cam.position.getValue()
# Store a copy of the original view to be restored in the case of user
# selecting Reset or Cancel.
self.original_view = coin.SbRotation(self.view.getValue())
self.original_pos = coin.SbVec3f(self.pos.getValue())
self.config_direction(0)
def reset(self):
# Reset the view to the original one.
self.cam.orientation = self.original_view
self.cam.position = self.original_pos
self.internal = True
for sld in self.sliders:
sld.setValue(0)
self.internal = False
for tbox in self.line_edits:
tbox.setText("0")
self.config_direction(0)
def cancel(self):
self.reset()
self.close()
def config_direction(self, i):
# Evaluate the vectors corresponding to the three directions for the
# current view, and assign the i-th one to self.direction.
self.view = self.cam.orientation.getValue()
self.view = coin.SbRotation(self.view.getValue())
self.pos = self.cam.position.getValue()
self.pos = coin.SbVec3f(self.pos.getValue())
up = coin.SbVec3f(0,1,0)
self.up = self.view.multVec(up)
out = coin.SbVec3f(0,0,1)
self.out = self.view.multVec(out)
u = self.up.getValue()
o = self.out.getValue()
r = (u[1]*o[2]-u[2]*o[1], u[2]*o[0]-u[0]*o[2], u[0]*o[1]-u[1]*o[0])
self.right = coin.SbVec3f(r)
self.direction = [self.right, self.up, self.out][i]
def check(self, i):
# Check if the direction of rotation has changed, if so then set
# previous slider & textbox to zero, and setup the new direction.
if i != self.current:
self.internal = True
self.sliders[self.current].setValue(0)
self.line_edits[self.current].setText("0")
self.internal = False
self.current = i
self.config_direction(i)
def rotate(self, value):
# Carry out the desired rotation about self.direction.
val = value*pi/180.0
rot = coin.SbRotation(self.direction, -val)
nrot = self.view*rot
prot = rot.multVec(self.pos - self.centre) + self.centre
self.cam.orientation = nrot
self.cam.position = prot
def valueChange(self, value):
# Respond to the change in value of a slider, update the corresponding
# text box, check for a direction change then rotate
# if the value was changed internally, ignore event.
if self.internal:
return
sender = self.sender()
for i in range(3):
if sender == self.sliders[i]:
break
self.line_edits[i].setText(str(value))
self.check(i)
self.rotate(value)
def valueEntered(self):
# Respond to a value being entered in a text box, updating the
# corresponding slider, check for direction change then rotate.
sender = self.sender()
for i in range(3):
if sender == self.line_edits[i]:
break
value = int(self.line_edits[i].text())
self.internal = True
self.sliders[i].setValue(value)
self.internal = False
self.check(i)
self.rotate(value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# We need to set a variable, otherwise, the dialog doesn't appear.
rotate = RotateGui()
Option
At the end of the function 'initUI' the first two arguments (right-300, 0) (line 91) provide the position for the top left corner of the window - my experience is that the behaviour was as intended on Ubuntu but Vista positioned the window too high and the 0 needed to be changed to ~30.
self.setGeometry(right-300, 0, 300, 150)
Forum
