Macro Perpendicular To Wire/fr
| Description |
|---|
| Cette macro positionne un objet perpendiculairement à la polyligne sélectionnée. Version macro : 00.03 Date dernière modification : 2020-03-31 Version FreeCAD : Toutes Téléchargement : Icône de la barre d'outils. Auteur: Mario52 |
| Auteur |
| Mario52 |
| Téléchargement |
| Icône de la barre d'outils. |
| Liens |
| Page des macros Comment installer une macro Comment créer une barre d'outils |
| Version Macro |
| 00.03 |
| Dernière modification |
| 2020-03-31 |
| Version(s) FreeCAD |
| Toutes |
| Raccourci clavier |
| None |
| Voir aussi |
| None |
Description
Description
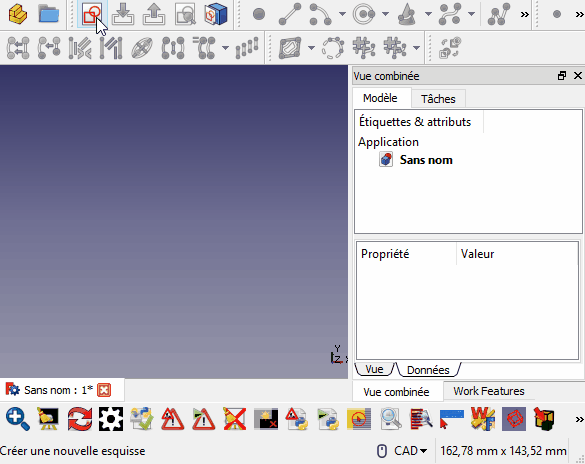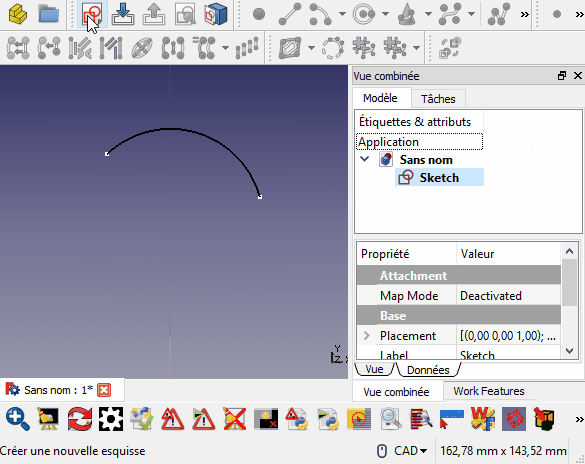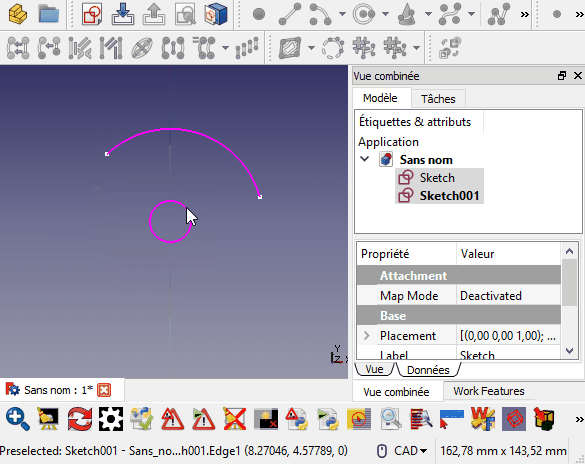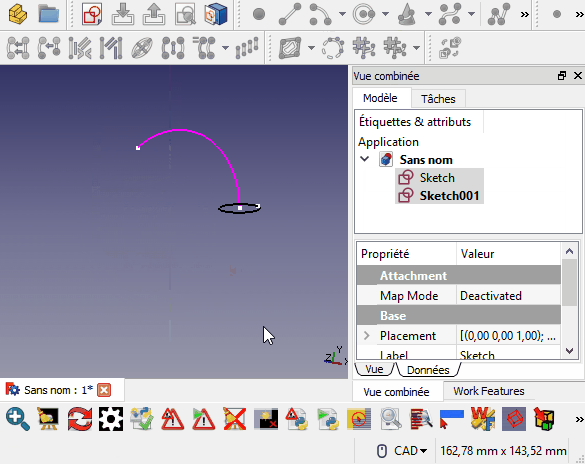
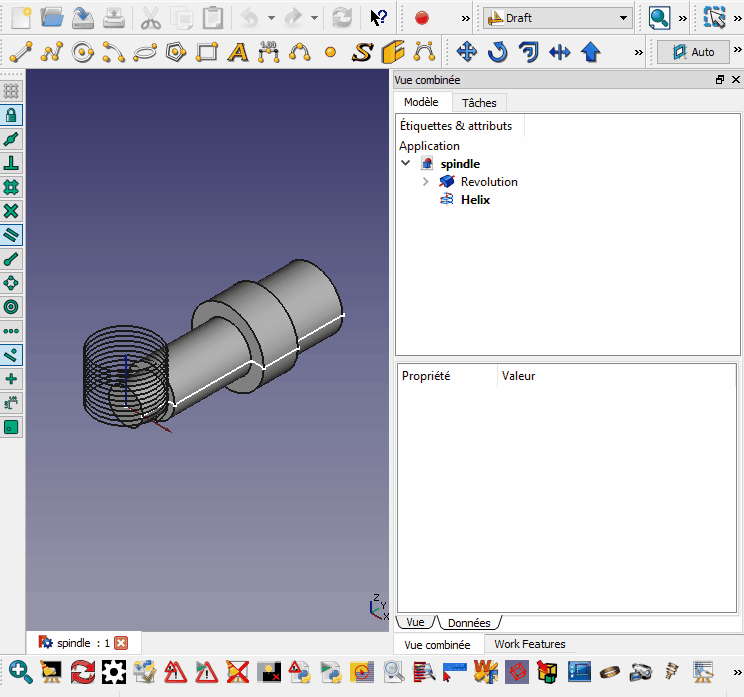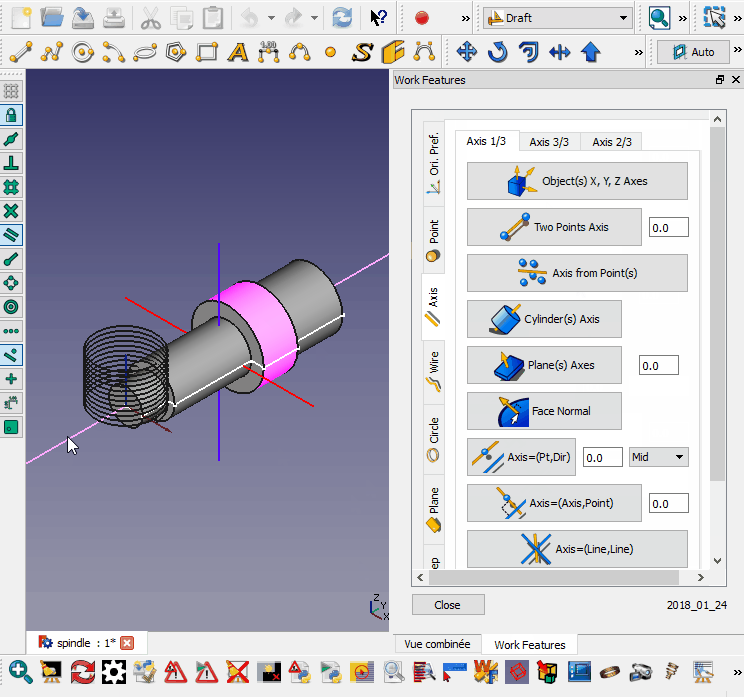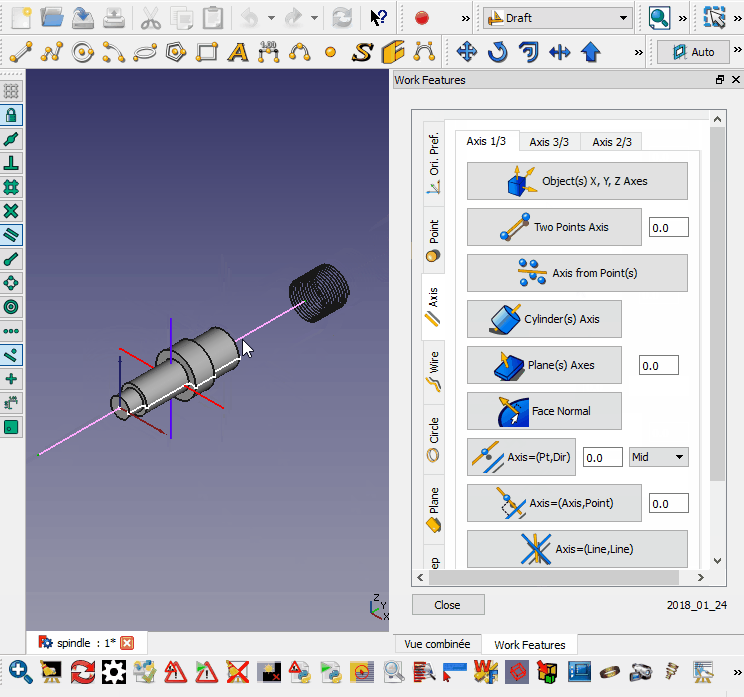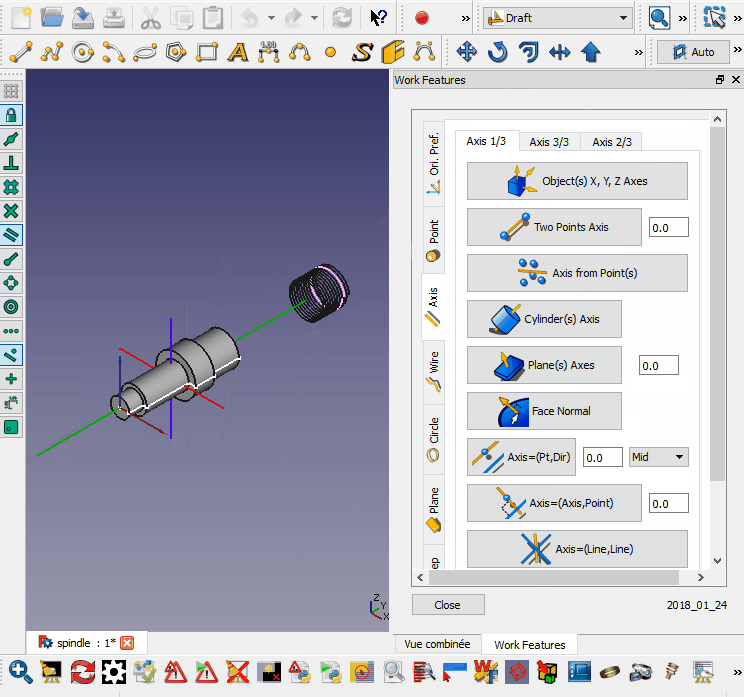
Cette macro place l'objet sélectionné perpendiculairement au fil sélectionné.
Utilisation
- Installez la macro via le
Gestionnaire des extensions
- Sélectionnez le chemin (peut être un élément ou un sous-élément)
- Sélectionnez l'objet à aligner
- Exécuter la macro
Script
L'icône de la macro dans la barre d'outils: ![]()
Macro Perpendicular To Wire.FCMacro
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__title__ = "Macro Perpendicular To Wire"
__author__ = "Mario52"
__url__ = "https://wiki.freecad.org/Macro_Perpendicular_To_Wire"
__version__ = "00.03"
__date__ = "31/03/2020"
import Draft, Part
try:
sel = FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelection() # Select an object
lineSelected = FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelectionEx()[0].SubObjects[0] # first object the Path object or SubObjects
myCircle = sel[1] # second object
pointsDirection = []
pointsDirection = lineSelected.discretize(Number=500) # discretize the path line first selection
v=pointsDirection[0].sub(pointsDirection[1]) # avec vecteurs 1 et 2 (direction debut ligne)
r=App.Rotation(App.Vector(0,0,1),v)
pl=FreeCAD.Placement() # placement object
pl.Rotation.Q = r.Q
pl.Base = pointsDirection[0]
myCircle.Placement = pl
del pointsDirection[:]
FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.recompute()
except Exception:
print( "Select two objects. 1:The path 2:The object to align" )
Options
Essentiellement, la ligne est coupée en x points avec discretize() (pour nos besoins, nous utilisons par défaut Number=500 mais les coupes peuvent être modulées entre 0 et 499)
pointsDirection = lineSelected.Shape.discretize(Number=500) # discretize the path line first selection
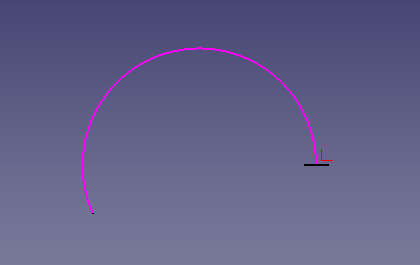
1. La perpendicularité est calculée entre 2 points:
v=pointsDirection[0].sub(pointsDirection[1]) # perpendicular of first > second point
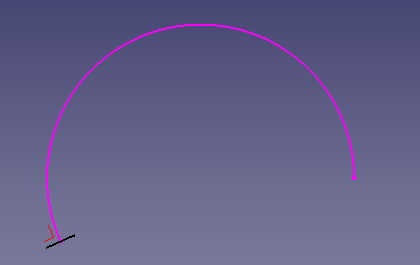
2:
v=pointsDirection[-1].sub(pointsDirection[-2]) # perpendicular of last > before last point
pl.Base = pointsDirection[-1] # position base last point
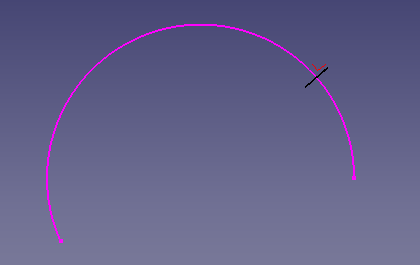
3:
v=pointsDirection[100].sub(pointsDirection[101]) # perpendicular of point 100 > point 101
pl.Base = pointsDirection[100] # position base point 100
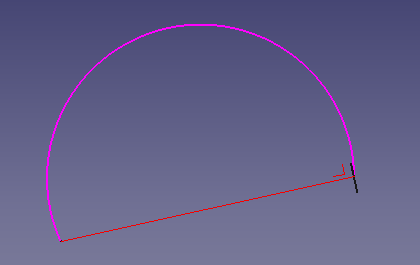
4:
v=pointsDirection[0].sub(pointsDirection[-1]) # perpendicular of first point > last point
pl.Base = pointsDirection[0] # position base first point
Les autres paramètres de discretize() sont les suivants:
# Discretizes the edge and returns a list of points.
# Forum thread: https://forum.freecad.org/viewtopic.php?f=12&t=16336#p129468
# The function accepts keywords as argument:
# discretize(Number=n) => gives a list of 'n' equidistant points
# discretize(QuasiNumber=n) => gives a list of 'n' quasi equidistant points (is faster than the method above)
# discretize(Distance=d) => gives a list of equidistant points with distance 'd'
# discretize(Deflection=d) => gives a list of points with a maximum deflection 'd' to the edge
# discretize(QuasiDeflection=d) => gives a list of points with a maximum deflection 'd' to the edge (faster)
# discretize(Angular=a,Curvature=c,[Minimum=m]) => gives a list of points with an angular deflection of 'a'
# and a curvature deflection of 'c'. Optionally a minimum number of points
# can be set which by default is set to 2.
Exemples
Discussions
- Discussion sur le forum [Spiralbohrer]
- https://forum.freecad.org/viewtopic.php?f=12&t=16336#p129468
Version
Ver 00.03 2020-03-21: Corrections de fautes dans le code source et de commentaires Ver 00.02 2019-04-06 : Python 3