Part Boolean/es
|
|
| Ubicación en el Menú |
|---|
| Part → Booleans |
| Entornos de trabajo |
| Part |
| Atajo de teclado por defecto |
| Ninguno |
| Introducido en versión |
| - |
| Ver también |
| Part Union, Part Common and Part Cut |
Este comando es una herramienta genérica todo-en-uno de operaciones booleanas. Te permite especificar que operación realizar y que parámetros utilizar a través del letrero de diálogo de abajo. Para operaciones booleanas, mira también Part Union, Part Common y Part Cut.
The Part Boolean command can perform four boolean operations. A task panel is used to specify the operation and the objects.
For quicker access to the boolean operations, use Part Cut,
Part Fuse,
Part Common and
Part Section.
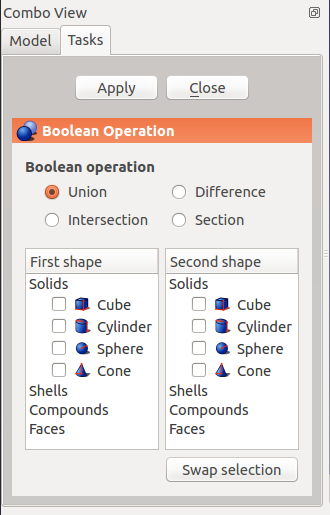
The Boolean Operation task panel
Usage
- Optionally select one or two shapes.
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
Boolean Operation button.
- Select the Part → Boolean →
Boolean Operation option from the menu.
- Press the
- The Boolean Operation task panel opens.
- Selected shapes are already checked in the shape lists.
- Select the appropriate Boolean Operation. Union, Difference, and intersection only accept solid shapes, Section also accepts non-solid shapes.
- Optionally (un)check an item in the First shape list.
- Optionally (un)check an item in the Second shape list.
- Optionally press the Swap Selection button to swap the shapes. This only makes sense for the Difference operation, as its result depends on the order.
- Do one of the following:
- Press the Apply button to confirm:
- A Fuse, Cut, Common, or Section object is created according to the selected operation.
- Optionally keep creating boolean objects.
- Press the Close button to close the task panel and finish the command.
- Press the Apply button to confirm:
Coplanar problems
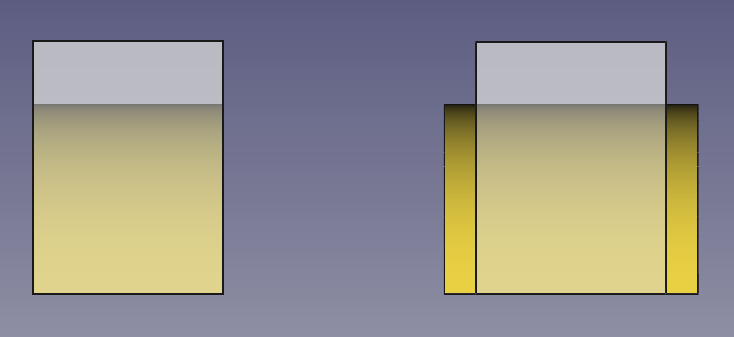
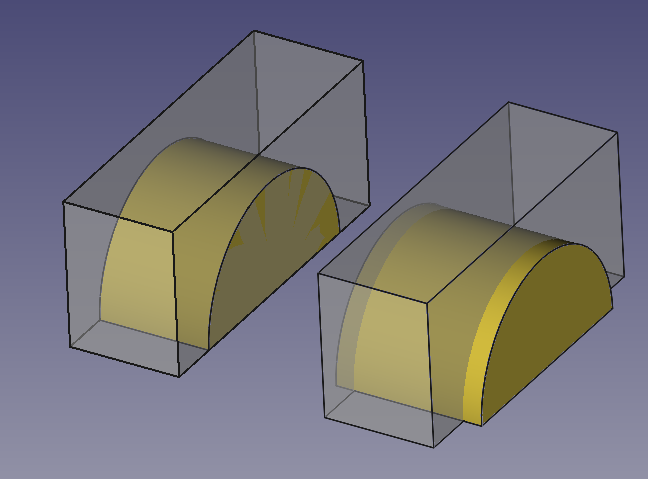
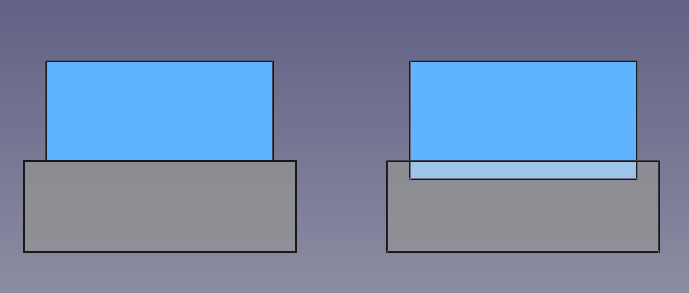
The boolean operations are performed by the internal geometry kernel, OpenCASCADE Technology (OCCT). This library sometimes has problems producing boolean results when the input objects share an edge or a face. To be sure the boolean operation is successful the recommendation is that the shapes intersect each other clearly; this means that in most cases, one shape should protrude or be larger in size than the other shape.
In cases of coplanarity, even if the first boolean operation succeeds, subsequent boolean operations may fail. In this case, the problem may not be in the last operation done, but in the older ones, that is, in the nested operations as indicated in the Tree View. To troubleshoot these issues, it is recommended to use the Part CheckGeometry command to inspect all objects for problems.
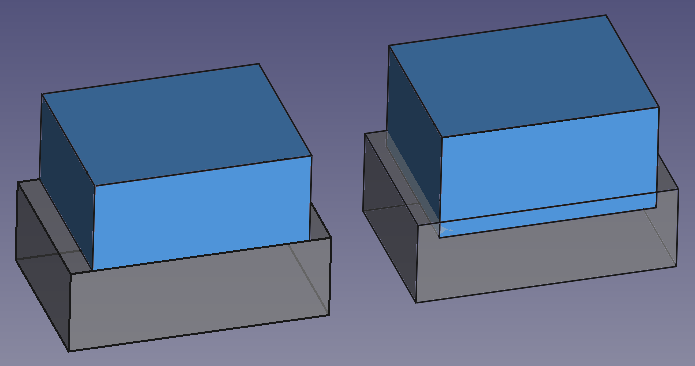
Left: shapes that share a face, a boolean cut may produce incorrect results. Right: shapes that intersect each other clearly, the boolean cut will be successful in most cases.
Left: shapes that share a face, a boolean union may produce incorrect results. Right: shapes that intersect each other clearly, the boolean union will be successful in most cases.
- Primitives: Box, Cylinder, Sphere, Cone, Torus, Tube, Create primitives, Shape builder
- Creation and modification: Create sketch, Extrude, Revolve, Mirror, Scale, Fillet, Chamfer, Make face from wires, Ruled Surface, Loft, Sweep, Section, Cross sections, 3D Offset, 2D Offset, Thickness, Projection on surface, Color per face
- Boolean: Make compound, Explode compound, Compound Filter, Boolean, Cut, Union, Intersection, Connect objects, Embed object, Cutout for object, Boolean fragments, Slice apart, Slice to compound, Boolean XOR, Check geometry, Defeaturing
- Other tools: Import CAD file, Export CAD file, Box selection, Create shape from mesh, Create points object from geometry, Convert to solid, Reverse shapes, Create simple copy, Create transformed copy, Create shape element copy, Refine shape, Set tolerance, Persistent section cut, Attachment…
- Preferences: Preferences, Fine tuning
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub