Cables CompoundPath/de
|
|
| Menüeintrag |
|---|
| Leitungsverläufe → Verbundverlauf |
| Arbeitsbereich |
| Cables |
| Standardtastenkürzel |
| C P |
| Eingeführt in Version |
| 0.2.0 |
| Siehe auch |
| Cables Leitungsverlauf |
Beschreibung
Der Befehl Cables Verbundverlauf ist dazu gedacht, ein Linienzugobjekt zu erstellen, das auf einer Gruppe anderer Linienzugobjekte basiert. Seine topologische Form ist ein Verbund aus Linienzugformen oder eine einzelne Linienzugform.
Es ist möglich den Verbundverlauf als Basis für Leitungen oder Leitungsführungen zu verwenden. Die richtige Kombination von Leitungsverläufen und Verbundverläufen kann eingesetzt werden, um den Erstellungsprozess komplexer Leitungsbündel oder Leitungen in Leitungsführungen, wie Kabelkanälen oder Installationsrohren, zu vereinfachen und unnötige redundante Basislinienzüge zu vermeiden. Ein einzelner Leitungsverlauf (WireFlex-Objekt) kann Bestandteil mehrerer verschiedener Verbundverläufe (CompoundPath-Objekte) sein und deren Form beeinflussen.
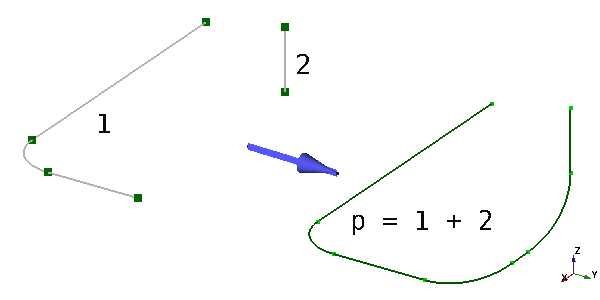
Das folgende Beispiel illustriert den Hauptzweck und die Möglichkeiten von '‘’Verbundverläufen -Objekt. Die Quelldatei des Beispiels kann hier heruntergeladen werden: compoundPath_Test2.FCStd.
Verbundverlauf aus zwei auseinanderliegenden Linienzügen aufgebaut
Der Verbundverlauf kann nicht wie der Leitungsverlauf direkt bearbeitet werden. Seine Form ist das Ergebnis von Algorithmen hinter den Werten der Eigenschaft Path Type: Complex, Wire (Linienzug) oder Simple (einfach) und anderen zusätzlichen Eigenschaften, die seine Basis-Linienzüge verarbeiten, die unter der Eigenschaft Links angegeben sind.
Path Type: Complex
Der Algorithmus Path Type:Complex erstellt eine einzige Leitungsform basierend auf allen in der Eigenschaft Links und teilweise auf ihrer Eigenschaft Points. Daher ist die Verwendung dieses Algorithmus nur möglich, wenn alle in Links aufgeführten Basisobjekte die Eigenschaft Points besitzen. Andernfalls schlägt er fehl. Zusätzlich nutzt der Algorithmus andere Eigenschaften, um die Absichten des Benutzers zu „erraten” und die gewünschte Form zu erstellen.
Hier sind einige Regeln, die vom Algorithmus verwendet werden:
- Lücken zwischen Basisobjekten sind zulässig. Sie werden automatisch mit Linien und Bögen oder Bézier-Kurven verbunden. Zur Herstellung der Verbindung wird ein kleinerer Abstand zwischen den Enden der Basisobjekte gewählt.
- Die Richtung eines einzelnen Basisobjekts ist nicht wichtig. Die Basisobjekte werden in der Reihenfolge der Eigenschaft Links verbunden.
- Wenn zwischen den Basisobjekten keine Lücke vorhanden ist, wird die Verbindung mit Bogenverrundungen korrigiert.
- Wenn Eigenschaften für Verbindungsversatz verwendet werden, werden die Begrenzungskanten der Basisobjekte verschoben, um den Versatzpunkt zu erreichen.
- Wenn zwei aufeinanderfolgende Linienkanten eine einzelne Linie bilden, werden sie durch eine einzelne Kante ersetzt.
- Die Tangentialität wird nach Möglichkeit über alle Verbindungen hinweg beibehalten (z. B. wenn MinimumFilletRadius dies zulässt).
Path Type: Wire
Der Algorithmus Path Type:Wire (Linienzug) erstellt eine einzelne Linienzugform aus der Eigenschaft Points aller Objekte, die in der Eigenschaft Links aufgeführt sind. Daher ist die Verwendung dieses Algorithmus nur möglich, wenn alle in Links aufgeführten Basisobjekte über die Eigenschaft Points verfügen. Andernfalls schlägt er fehl. Er erzeugt einen Linienzug basierend auf bestimmten Punkten, ähnlich wie es der Befehl ![]() Draft Linienzug tun würde.
Draft Linienzug tun würde.
Die vom Algorithmus verwendeten Regeln ähneln denen des Path Type:Complex, mit Ausnahme der Verwendung einer Bézier-Kurve. Die einzigen zulässigen Kantenformen in diesem Modus sind Linien und Bögen. Wenn das Basisobjekt andere Formen enthält (z. B. B-Spline), werden diese durch die beiden oben genannten ersetzt.
Path Type: Simple
Der Algorithmus Path Type:Simple erzeugt einen Verbund von Linienzugformen, die in der Eigenschaft Links aufgelistet werden. Er erzeugt genau das gleiche Ergebnis, wie es der Befehl Part Verbund tun würde.
Hier können beliebige linienzugartige Objekte (siehe Hinweis 1) als Basis für die Form eines Verbundverlaufs verwendet werden, ohne Garantie für eine erfolgreiche Erstellung des richtigen Linienzuges, der sich als Basis für eine Leitung oder eine Leitungsführung eignet. Für die erfolgreiche Erstellung solch eines Linienzuges (für eine Leitungsführung) müssen sich die Basisformen an ihren Endknoten berühren und zusätzlich (um als Basis einer Leitung verwendet werden zu können) müssen sie korrekt angeordnet sein, d. h. der erste Knoten der ersten Form muss der Anfang des Verbundverlaufs sein und der letzte Knoten der letzte Form muss das Ende des Verbundverlaufs sein.
Mit dem Algorithmus Simple werden keine zusätzlichen automatischen Aktionen durchgeführt. Wenn beispielsweise tangentiale Verbindungen zwischen Basisformen erforderlich sind, müssen diese manuell hergestellt werden.
Der Algorithmus Simple kann verwendet werden, wenn die Ergebnisse der Algorithmen Complex oder Wire nicht zufriedenstellend sind. Unter Berücksichtigung der oben genannten Regeln kann eine Reihe miteinander verbundener Skizzen, die frei im 3D-Raum ausgerichtet sind, beispielsweise als Basisformen für einen Verbundverlauf verwendet werden.
Anwendung
- Mindestens zwei vorhandene Linienzugobjekte (siehe Hinweis 1) in der 3D-Ansicht oder der Baumansicht auswählen.
- Einen Verbundverlauf mit einer der folgenden Methoden erstellen:
- Die Schaltfläche
Verbundverlauf button.
- Den Menüeintrag Leitungsverläufe →
Verbundverlauf auswählen.
- Ein Rechtsklick in die Baumansicht oder die 3D-Ansicht und die Menüoption Leitungsverläufe →
Verbundverlauf im Kontextmenü auswählen.
- Die Schaltfläche
Beispiel
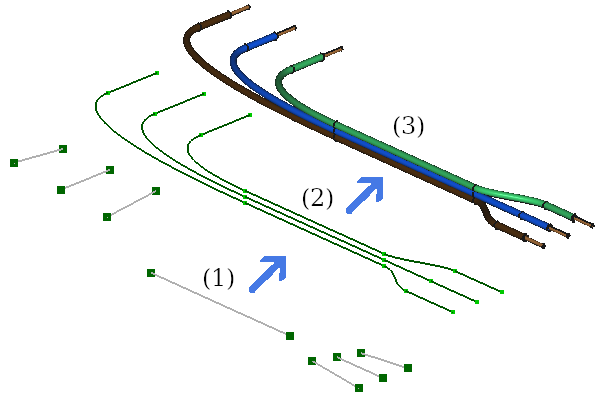
Das Beispiel zeigt, wie man drei verschiedene Verbundverläufe durch Verwendung von Basislinienzügen, die den Anfang, die Mitte und das Ende des Verlaufs markieren. Lücken zwischen einzelnen Linienzügen werden automatisch gefüllt. Zusätzlich wird der mittlere Linienzug von allen drei Pfaden mit einem unterschiedlichen Versatz verwendet. Details findet man in der Beispieldokumentdatei: compoundPath_x3.FCStd.
(1) Einzelne Basislinienzüge, (2) 3 Verbundverläufe mit Versatz, aus den Basislinienzügen aufgebaut, (3) Leitungen basierend auf den Verbundverläufen
Hinweise
- Hinweis 1: die folgenden Linienzugobjekte können gefahrlos als Basis ausgewählt werden: Leitungsverlauf (WireFlex-Objekt), Draft-Linienzug oder ein anderer vorhandener Verbundverlauf. Andere Objekte, die eine Eigenschaft Points besitzen (z. B. Draft-B-Spline, Draft-Bézierkurve) können auch verwendet werden, aber die Ergebnisse können anders als erwartet ausfallen (besonders dann, wenn der Wert der Eigenschaft Path Type
Complexist). Der Einsatz anderer Objekte (z. B. Skizzen) kann erfolgreich sein, wenn der Wert der Eigenschaft Path TypeSimpleist. Allerdings kann die Erstellung einer Leitung oder einer Leitungsführung fehlschlagen, wenn z. B. Lücken zwischen solchen Objekten vorhanden sind. - Hinweis 2: Es können unerwartete Ergebnisse oder Fehler auftreten, besonders wenn die Eigenschaft Connection Offset Dist mit relativ großen Werten verwendet wird. Es wird empfohlen, eine Fehlersuche bei einer solchen Form damit zu beginnen, dass Connection Offset Dist auf 0 gesetzt wird und andere Parameter auf Werte dicht an ihren Standardwerten; dann werden die Werte in kleinen Schritten erhöht, um nachzuvollziehen, was passiert.
Eigenschaften
Daten
Base
- Daten-EigenschaftLinks (
LinkList): Enthält eine Liste der Objekte, die zu einem Verbundverlauf (CompoundPath) hinzugefügt wurden
Compound Path
- Daten-EigenschaftConnection Offset Angle (
Angle): Legt den Winkel einer connection offset distance fest. - Daten-EigenschaftConnection Offset Dist (
Length): Legt den Abstand des versetzten Punktes zum berechneten Verbindungspunkt der Endkanten von zwei aufeinanderfolgenden Basislinienzügen fest. Dieser wird verwendet, um z. B. unterschiedliche Verbundverläufe aufeinander abzustimmen, die auf demselben Basislinienzug in einer Leitungsführung basiseren. - Daten-EigenschaftConnection Type (
Enumeration): Legt die Art der Kurven fest, die zum verbinden von Basislinienzügen eingesetzt werden. Mögliche Werte sind:ArcoderBez. Gilt nur für Path TypeComplex. - Daten-EigenschaftDegree (
Integer): Legt den Grad einer Bézierfunktion fest, die in der Eigenschaft Connection Type eingesetzt wird. - Daten-EigenschaftEdge With Smallest Bending Radius (
String): (schreibgeschützt) Zeigt den Namen der Kante an, die den geringsten Radius enthält oder den vorausgehenden geringsten Radius, wenn dieser 0 ist. Er kann zusammen mit Smallest Bending Radius eingesetzt werden, um die Kante mit dem kleinsten Biegeradius zu finden und diesen mit der Vorgabe für die Leitung zu vergleichen, die auf seiner Grundlage erstellt wird. - Daten-EigenschaftLength (
Length): Legt die Länge dieses Verbundverlaufs fest. - Daten-EigenschaftMinimum Fillet Radius (
Length): Legt den Mindestradius für die Verrundung von Verbindungsstellen zwischen den Basislinienzügen fest. Der tatsächliche Radius darf länger sein, wenn erforderlich. - Daten-EigenschaftPath Type (
Enumeration): Legt die Ausführungsart der Form des Verbundverlauf shape. Mögliche Werte sind:Complex,Wire(Linienzug) oderSimple(einfach). Sie werden in der Beschreibung vorgestellt. - Daten-EigenschaftPoints (
VectorList): Legt die Punkte des Verbundverlaufs in seinem lokalen Koordinatensystem fest. - DatenRatio (
Float): Legt die Verhältnisse von Abschnitten in der Kurve fest, die in der Lücke zwischen Basislinienzügen erstellt wird. Normalerweise ergibt ein Wert zwischen 1 und 2 die besten Ergebnisse. - Daten-EigenschaftSmallest Bending Radius (
Length): (schreibgeschützt) Zeigt den kleinsten erkannten Radius aller Kanten an.