Part Offset/en
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Part → 3D Offset |
| Workbenches |
| Part |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| Part Thickness, Part 2D Offset |
Description
The Part Offset command creates parallel copies of a selected shape at a certain distance from the base shape, giving a new object.
Usage
- Select an object to offset.
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
3D Offset button.
- Select the Part →
3D Offset option from the menu.
- Press the
- An Offset object is created and the Offset task panel opens.
- Adjust distance and parameters depending on the original object and the resulting objects validity.
- Press OK to close the task panel.
Notes
- App Link objects linked to the appropriate object types and App Part containers with the appropriate visible objects inside can also be used as source objects.
- As noted in the OCC documentation and mentioned in the Properties section, some options are not implemented yet.
Examples
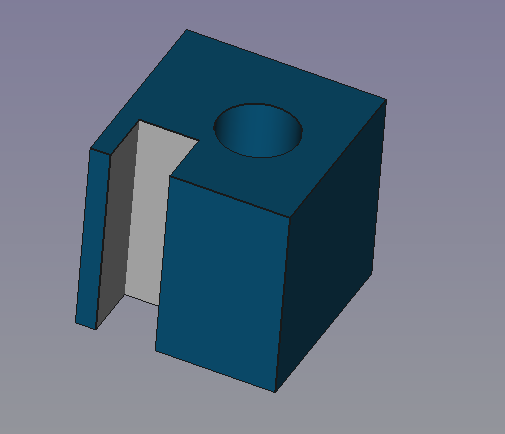
Object with small offset and rounded (arc) corners.
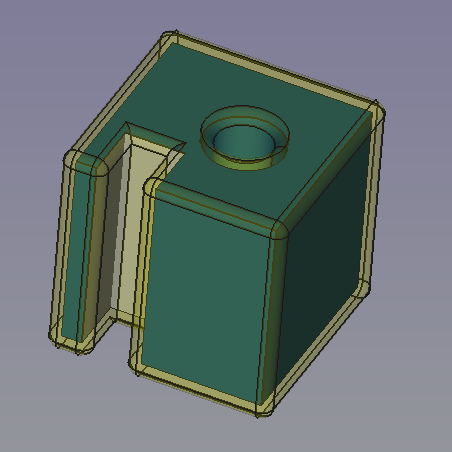
Same object with sharp (intersection) corners.
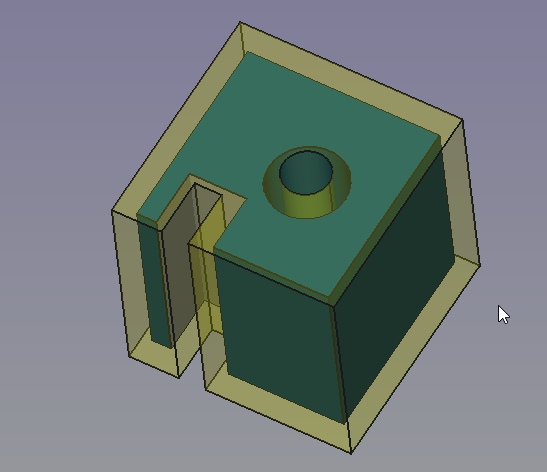
Same object with thick distance overfilling the front left gap and allowed intersections.
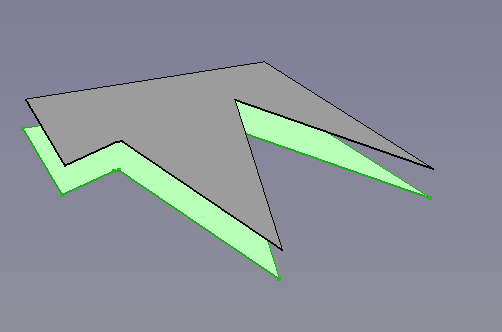
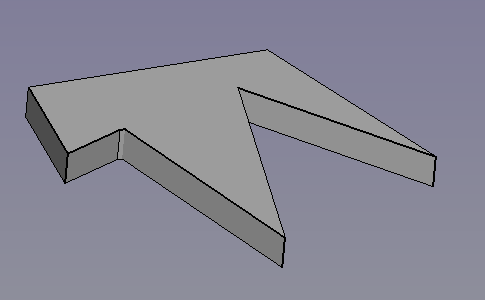
Arbitrary shape (Draft Wire) with a 3D Offset (ignores MODE parameter).
Same shape with a 3D Offset as SKIN and filled offset.
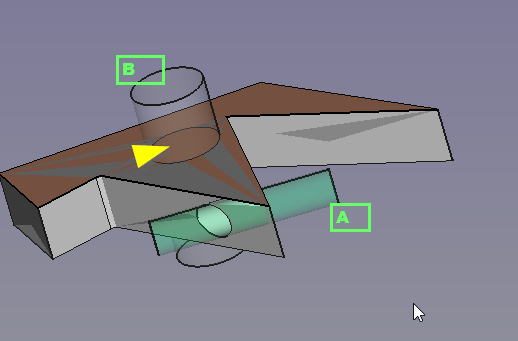
Filled offset with 2 Cylinders creating boolean cuts. Cylinder A goes through the FILL whilst Cylinder B only goes through the FILL and NOT through the source 2D shape.
Properties
Offset
- DataSource: Source shape.
- DataValue: Distance to offset the faces of the source shape.
- DataMode: Mode of creation. Only the Skin mode is currently implemented in OCC so the other two modes have no effect.
- DataJoin: How the new corners are build up. Intersection gives sharp corners by linear extension of the edges. Arc and Tangent give rounded corners.
- DataIntersection: Allows offsets pointing inwards to "overflow" the gap by intersecting the resulting shape until opposite faces are reached.
- DataSelf Intersection: Not yet implemented in OCC and thus should be left with the default value (false).
- DataFill Offset: When the shape was 2 dimensional, the gap between the 2 shapes gets filled. The fill is now a solid, hence the source shape is not a solid. Thus boolean operations may lead to strange results (see example above).
- Primitives: Box, Cylinder, Sphere, Cone, Torus, Tube, Create primitives, Shape builder
- Creation and modification: Create sketch, Extrude, Revolve, Mirror, Scale, Fillet, Chamfer, Make face from wires, Ruled Surface, Loft, Sweep, Section, Cross sections, 3D Offset, 2D Offset, Thickness, Projection on surface, Color per face
- Boolean: Make compound, Explode compound, Compound Filter, Boolean, Cut, Union, Intersection, Connect objects, Embed object, Cutout for object, Boolean fragments, Slice apart, Slice to compound, Boolean XOR, Check geometry, Defeaturing
- Other tools: Import CAD file, Export CAD file, Box selection, Create shape from mesh, Create points object from geometry, Convert to solid, Reverse shapes, Create simple copy, Create transformed copy, Create shape element copy, Refine shape, Set tolerance, Persistent section cut, Attachment…
- Preferences: Preferences, Fine tuning
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub