Std Part/ko
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| None |
| Workbenches |
| All |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| 0.17 |
| See also |
| Std Group, PartDesign Body |
설명
부품그릇(내부적으로 App Part라고 함)은 여러 개체를 한 곳에 담아 3D 보기에서 한번에 이동할 수 있게 하는 다목적 그릇입니다.
The Std Part element was developed to be the basic building block to create mechanical assemblies. In particular, it is meant to arrange objects that have a Part TopoShape, like Part Primitives, PartDesign Bodies, and other Part Features. The Std Part provides an Origin object with local X-, Y-, and Z-axis, and standard planes, that can be used as reference to position the contained objects. In addition, Std Parts may be nested inside other Std Parts to create a big assembly from smaller sub-assemblies.
Although it is primarily intended for solid bodies, the Std Part can be used to manage any object that has a Placement property, so it can also contain Mesh Features, sketches, and other objects derived from the App GeoFeature class.
Do not confuse the PartDesign Body with the
Std Part. The first one is a specific object used in the
PartDesign Workbench, intended to model a single contiguous solid by means of PartDesign Features. On the other hand, the Std Part is not used for modelling, just to arrange different objects in space, with the intention to create assemblies.
The Std Part tool is not defined by a particular workbench, but by the base system, thus it is found in the Structure toolbar that is available in all workbenches. To group objects arbitrarily without considering their position, use
Std Group; this object does not affect the placements of the elements that it contains, it is essentially just a folder that is used to keep the Tree View organized.
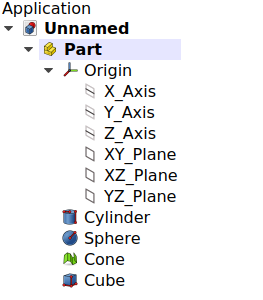
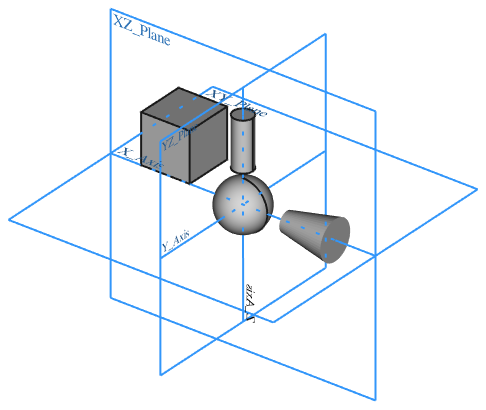
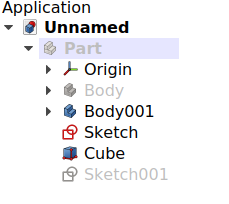
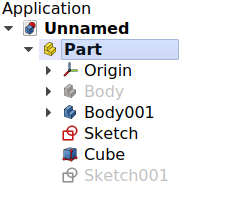
Left: elements inside a Std Part in the Tree View. Right: objects positioned in space, referred to the Origin of the Std Part.
Usage
- Press the
New Part button.
- An empty Part is created and automatically becomes active.
- To add objects to the Part, select them in Tree View, and drag and drop them onto the Part.
- To remove objects from the Part, drag them out of the Part, and onto the document label at the top of the Tree View.
- Objects can also be added and removed by editing the 데이터Group property of the Part.
Notes
- An object can only belong to a single Part.
- 3D operations like Part Boolean cannot be applied to Parts. For example, you cannot select two Parts, and perform a Part Fuse or Part Cut.
Properties
The Std Part, internally called App Part (App::Part class), is derived from the App GeoFeature (App::GeoFeature class) and inherits almost all its properties. It also has several additional properties. Notably properties that help it manage information in the context of an assembly, for example, 데이터Type, 데이터Id, 데이터License, 데이터LicenseURL and 데이터Group.
These are the properties available in the Property View. Hidden properties can be shown by using the Show hidden command in the context menu of the Property View.
See Part Feature for an explanation of some of the properties listed below.
Data
Base
- 데이터Type (
String): a description for this object. By default, it is an empty string"". - 데이터Material (
Link): the material for this object. - 데이터 (Hidden)Meta (
Map): map with additional meta information. By default, it is empty{}. - 데이터Id (
String): an identification or part number for this object. By default, it is an empty string"". - 데이터 (Hidden)Uid (
UUID): the universally unique identifier (UUID) (128-bit number) of the object. This is assigned at creation time. - 데이터License (
String): a field to specify the license for this object. By default, it is an empty string"". - 데이터License URL (
String): a field to specify the web address to the license or contract for this object. By default, it is an empty string"". - 데이터Color (
Color): a tuple of four floating point RGBA values to define the color of the object. - 데이터Placement (
Placement) - 데이터 (Hidden)_ Element Map Version (
String) - 데이터Label (
String) - 데이터 (Hidden)Label2 (
String) - 데이터 (Hidden)Expression Engine (
ExpressionEngine) - 데이터 (Hidden)Visibility (
Bool) - 데이터 (Hidden)Origin (
Link): the App Origin object that is the positional reference for all elements listed in 데이터Group. - 데이터Group (
LinkList): a list of referenced objects. By default, it is empty[]. - 데이터 (Hidden)_ Group Touched (
Bool): whether the group is touched or not.
Part
- 데이터 (Hidden)_ Part_ Shape Cache (
ShapeCache): Shape cache. Not available if 데이터Group is empty.
View
Base
- 보기 (Hidden)Transform Origin (
Placement)
Display Options
- 보기Display Mode (
Enumeration):Group. - 보기Show In Tree (
Bool) - 보기Visibility (
Bool)
Selection
- 보기On Top When Selected (
Enumeration) - 보기Selection Style (
Enumeration)
Detailed explanation
Active status
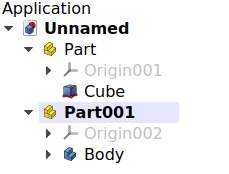
An open document can contain multiple Parts. But only one Part can be active. The active Part is displayed in the Tree View with the background color specified by the Active container object value in the Preferences Editor. It will also be shown with bold text.
To activate or de-activate a Part:
- Double click on it on the Tree View, or
- Open the context menu (right click) and select Active Object.
Document with two Std Parts, of which the second one is active.
Origin
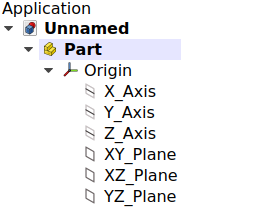
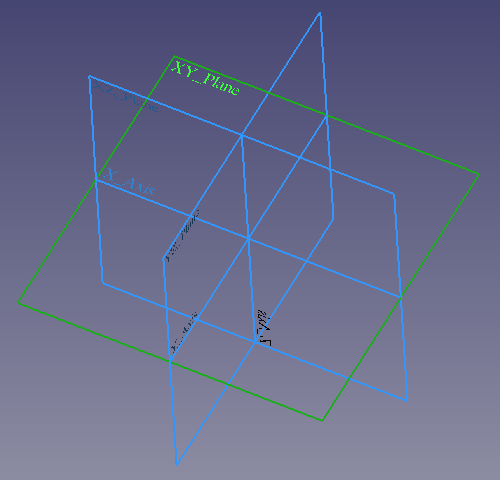
The Origin consists of the three standard axes (X, Y, Z) and three standard planes (XY, XZ and YZ). Sketches and other objects can be attached to these elements when creating them.
Left: Part Origin in the Tree View. Right: representation of the Origin elements in the 3D View.
Note: the Origin is an App Origin object (App::Origin class), while the axes and planes are objects of type App::Line and App::Plane respectively. Each of these elements can be hidden and unhidden individually with the Space bar; this is useful to choose the correct reference when creating other objects.
Note 2: all elements inside the Part are referenced to the Part's Origin which means that the Part can be moved and rotated in reference to the global coordinate system without affecting the placement of the elements inside.
Visibility management
The Part's visibility supersedes the visibility of any object it contains. If the Part is hidden, the objects it contains will be hidden as well, even if their individual 보기Visibility property is set to true. If the Part is visible, then each object's 보기Visibility determines whether the object is shown or not.
The visibility of the Std Part determines whether the objects grouped under it are shown in the 3D View or not. Left: the Part is hidden, so none of the objects will be shown in the 3D View. Right: the Part is visible, so each object controls its own visibility.
Scripting
See also: FreeCAD Scripting Basics and scripted objects.
See Part Feature for the general information on adding objects to the document.
A Std Part (App Part) is created with the addObject() method of the document. Once a Part exists, other objects can be added to it with the addObject() or addObjects() methods.
import FreeCAD as App
doc = App.newDocument()
part = App.ActiveDocument.addObject("App::Part", "Part")
obj1 = App.ActiveDocument.addObject("PartDesign::Body", "Body")
obj2 = App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Box", "Box")
part.addObjects([obj1, obj2])
App.ActiveDocument.recompute()
You cannot create a scripted App::Part. However, you can add App::Part behavior to a scripted Part::FeaturePython object by using the following code:
class MyGroup(object):
def __init__(self, obj=None):
self.Object = obj
if obj:
self.attach(obj)
def dumps(self):
return
def loads(self, _state):
return
def attach(self, obj):
obj.addExtension("App::OriginGroupExtensionPython")
obj.Origin = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.addObject("App::Origin", "Origin")
def onDocumentRestored(self, obj):
self.Object = obj
class ViewProviderMyGroup(object):
def __init__(self, vobj=None):
if vobj:
vobj.Proxy = self
self.attach(vobj)
else:
self.ViewObject = None
def attach(self, vobj):
vobj.addExtension("Gui::ViewProviderOriginGroupExtensionPython")
self.ViewObject = vobj
def dumps(self):
return None
def loads(self, _state):
return None
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::FeaturePython",
"Group",
MyGroup(),
ViewProviderMyGroup(),
True)
- File: New Document, Open, Open Recent, Close, Close All, Save, Save As, Save Copy, Save All, Revert, Import, Export,Merge Document, Document Information, Print, Print Preview, Export PDF, Exit
- Edit: Undo, Redo, Cut, Copy, Paste, Duplicate Object, Recompute, Box Selection, Box Element Selection, Select All, Delete, Send to Python Console, Placement, Transform, Align To, Toggle Edit Mode, Properties, Edit Mode, Preferences
- View:
- Miscellaneous: New 3D View, Orthographic View, Perspective View, Fullscreen, Bounding Box, Toggle Axis Cross, Clipping View, Texture Mapping, Toggle Navigation/Edit Mode, Material, Appearance, Random Color, Appearance per Face, Toggle Transparency, Workbench, Status Bar
- Standard Views: Fit All, Fit Selection, Align to Selection, Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric, Home, Front, Top, Right, Rear, Bottom, Left, Rotate Left, Rotate Right, Store Working View, Recall Working View
- Freeze Display: Save Views, Load Views, Freeze View, Clear Views
- Draw Style: As Is, Points, Wireframe, Hidden Line, No Shading, Shaded, Flat Lines
- Stereo: Stereo Red/Cyan, Stereo Quad Buffer, Stereo Interleaved Rows, Stereo Interleaved Columns, Stereo Off, Issue Camera Position
- Zoom: Zoom In, Zoom Out, Box Zoom
- Document Window: Docked, Undocked, Fullscreen
- Visibility: Toggle Visibility, Show Selection, Hide Selection, Select Visible Objects, Toggle All Objects, Show All Objects, Hide All Objects, Toggle Selectability
- Toolbars: File, Edit, Clipboard, Workbench, Macro, View, Individual Views, Structure, Help, Lock Toolbars
- Panels: Tree View, Property View, Model, Selection View, Python Console, Report View, Tasks, DAG View
- Overlay Docked Panel: Toggle Overlay for All Panels, Toggle Transparent Panels, Toggle Overlay, Toggle Transparent Mode, Bypass Mouse Events in Overlay Panels, Toggle Left, Toggle Right, Toggle Top, Toggle Bottom
- Link Navigation: Go to Linked Object, Go to Deepest Linked Object, Select All Links
- Tree View Actions: Sync View, Sync Selection, Sync Placement, Preselection, Record Selection, Single Document, Multi Document, Collapse/Expand, Initiate Dragging, Go to Selection, Selection Back, Selection Forward
- Tools: Addon Manager, Measure, Clarify Selection, Quick Measure, Units Converter, Load Image, Save Image, Text Document, View Turntable, Scene Inspector, Dependency Graph, Export Dependency Graph, Document Utility, Edit Parameters, Customize
- Macro: Record Macro, Macros, Recent Macros, Execute Macro, Attach to Remote Debugger, Debug Macro, Stop Debugging, Step Over, Step Into, Toggle Breakpoint
- Help: What's This, Start Page, Users Documentation, FreeCAD Forum, Report an Issue, Restart in Safe Mode, Developers Handbook, Python Modules Documentation, FreeCAD Website, Donate to FreeCAD, About FreeCAD
- Additional:
- Miscellaneous: New Part, New Group, Variable Set, Link Group, Select All Instances, Toggle Freeze
- Datums: Coordinate System, Datum Plane, Datum Line, Datum Point
- Link Actions: Make Link, Make Sub-Link, Replace With Link, Unlink, Import Link, Import All Links
- Expression Actions: Copy Selected, Copy Active Document, Copy All Documents, Paste
- Selection Filter: Vertex Selection, Edge Selection, Face Selection, No Selection Filters
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub