PartDesign WizardShaft
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Part Design → Shaft Design Wizard |
| Workbenches |
| PartDesign |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| None |
Description
This tool allows you to create a shaft from a table of values, and to analyse forces and moments.
Usage
You can start the wizard from the Part Design menu Part Design → Shaft Design Wizard.
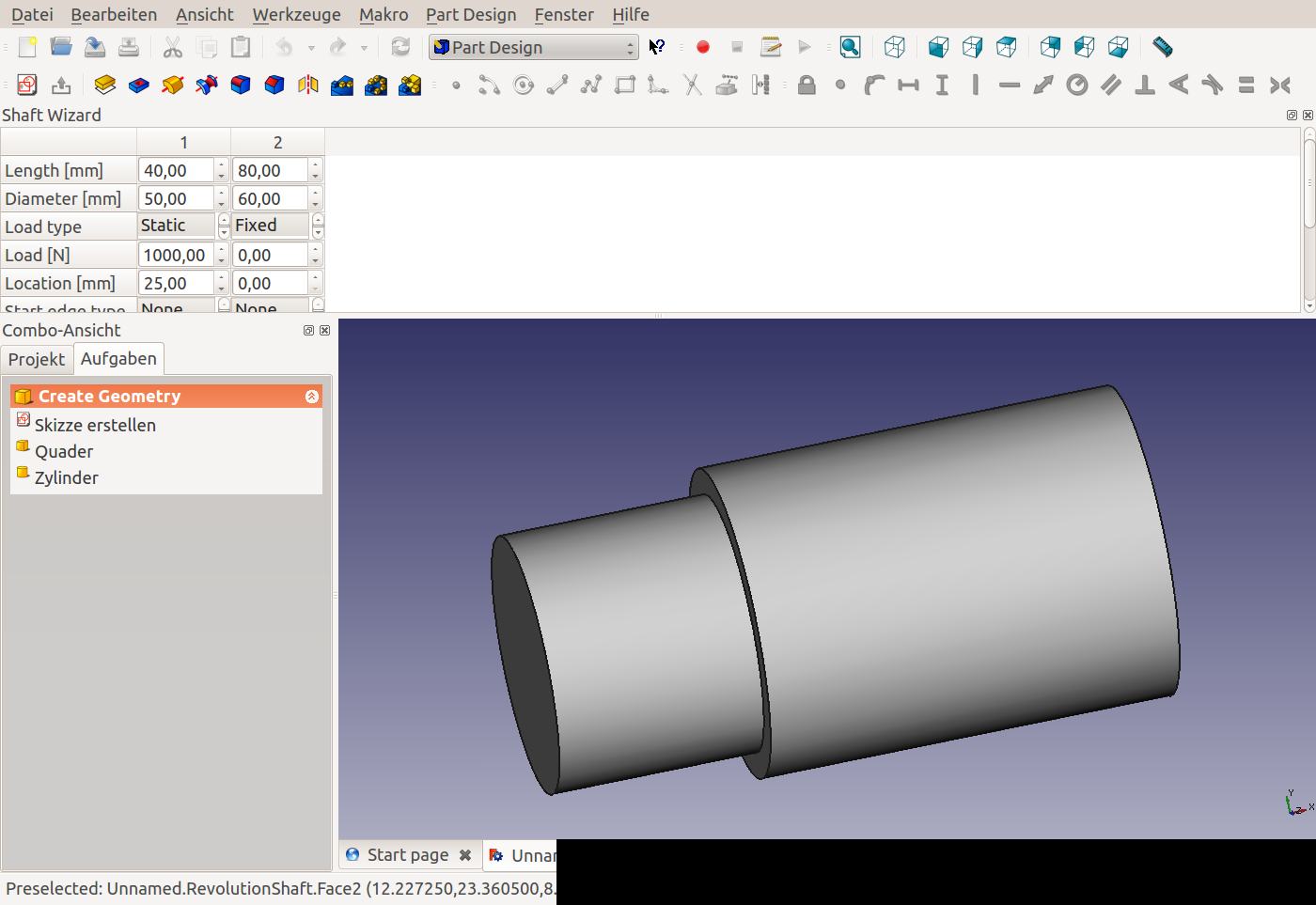
The wizard will start and show a default table, the corresponding shaft part and force/moment graphs.
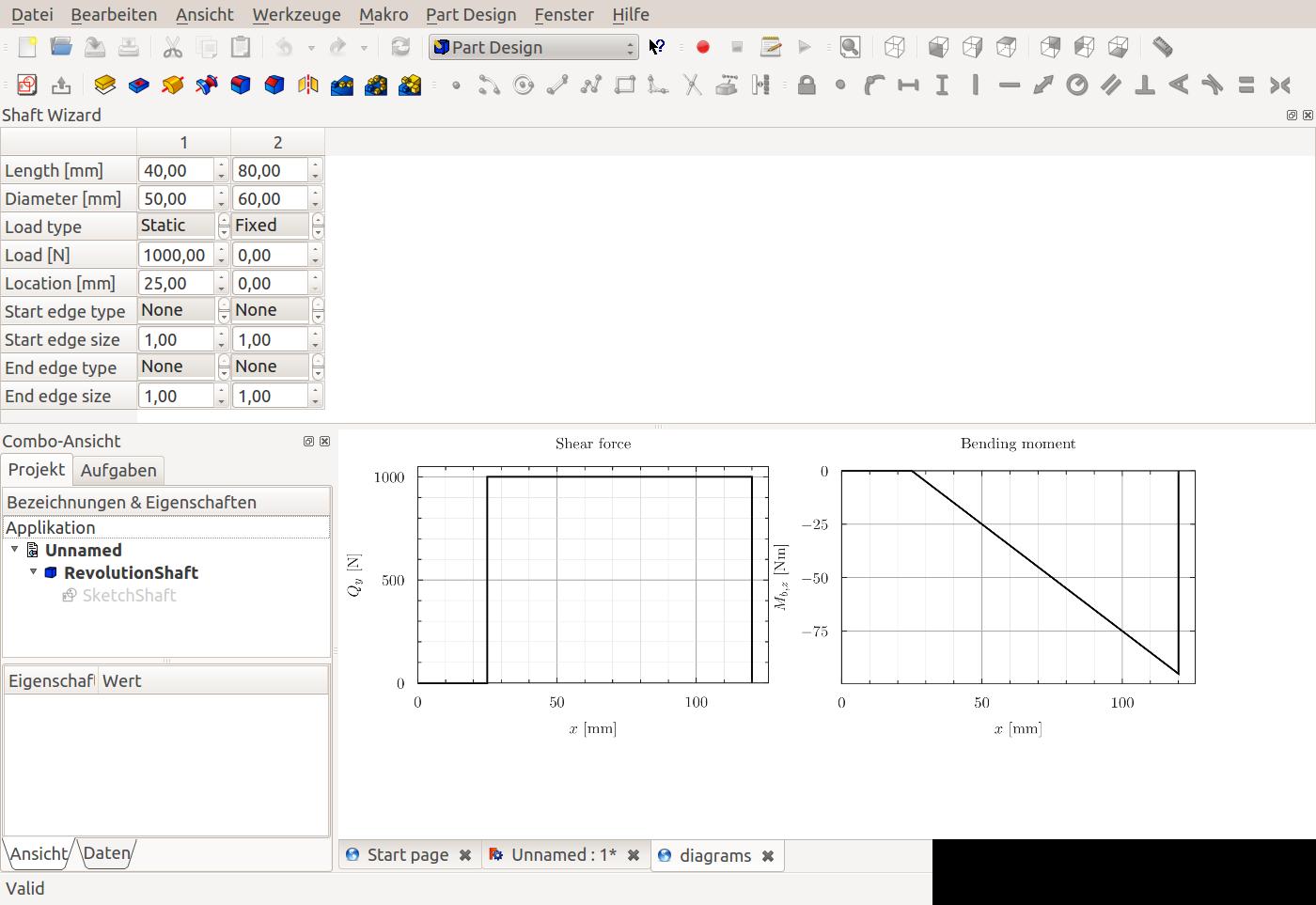
The top of the window is taken up by the table. It is organized into numbered columns which correspond to segments of the shaft. A shaft segment is characterized by having certain length and diameter. The main window shows two tabs. One is the shaft part itself (a revolution feature), shown in the image above. The second tab shows graphs of the shear forces and moments created by the loads defined in the table.
Prerequisites
The Shaft Design Wizard depends on the matplotlib library to create and display the graphs of shear force and bending moment. On Debian/Ubuntu-based systems, it is available through the python-matplotlib package.
Parameters
For each shaft segment, the following parameters can be defined
- Length of the segment
- Diameter of the segment
- Load type. Note that you have to click on the desired entry in the menu after scrolling to it, otherwise it will not be selected!
- None: No load
- Fixed: The end of the shaft is fixed (e.g. welded to another part). This load type can only be defined for the first or last segment.
- Static: There is a static load on this shaft segment
- Load on the shaft segment
- Location where the load is applied to the segment. The location is counted from the left-hand edge of the segment
(Other rows and load types exist but no functionality has been implemented yet)
Menus
To add a new shaft segment, right-click into the empty space to the right of the table, and choose "Add column".
Limitations
- It is not possible to have adjacent shaft segments with the same diameter.
Missing functionality
- Table-driven chamfers and rounds on the shaft edges
- Recognize a previously created Shaft Design Wizard part and initialize the table values from it
- Shaft stress calculation
- Visualization of loads on the shaft (can use the same functionality as for FEM module)
- Definition of loads as a Document Object (can use the same functionality as for FEM module)
- Material database
- Allow loads in the Z-direction as well as in Y-direction (requires definition of loads as a Document Object, otherwise the table will become very long)
- Helper tools: New Body, New Sketch, Attach Sketch, Edit Sketch, Validate Sketch, Check Geometry, Sub-Shape Binder, Clone
- Modeling tools:
- Additive tools: Pad, Revolution, Additive Loft, Additive Pipe, Additive Helix, Additive Box, Additive Cylinder, Additive Sphere, Additive Cone, Additive Ellipsoid, Additive Torus, Additive Prism, Additive Wedge
- Subtractive tools: Pocket, Hole, Groove, Subtractive Loft, Subtractive Pipe, Subtractive Helix, Subtractive Box, Subtractive Cylinder, Subtractive Sphere, Subtractive Cone, Subtractive Ellipsoid, Subtractive Torus, Subtractive Prism, Subtractive Wedge
- Boolean: Boolean Operation
- Dress-up tools: Fillet, Chamfer, Draft, Thickness
- Transformation tools: Mirror, Linear Pattern, Polar Pattern, Multi-Transform, Scale
- Additional tools: Shape Binder, Involute Gear, Sprocket, Shaft Design Wizard
- Context menu: Suppressed, Set Tip, Move Object To…, Move Feature After…
- Preferences: Preferences, Fine tuning
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub