EM FHPlane/de
|
|
| Menüeintrag |
|---|
| EM → FHEbene |
| Arbeitsbereich |
| EM |
| Standardtastenkürzel |
| E P |
| Eingeführt in Version |
| 0.17 |
| Siehe auch |
| EM FHKnoten, EM FHEbeneLoch, EM FHEbeneHinzufügenEntfernenKnotenLoch |
Beschreibung
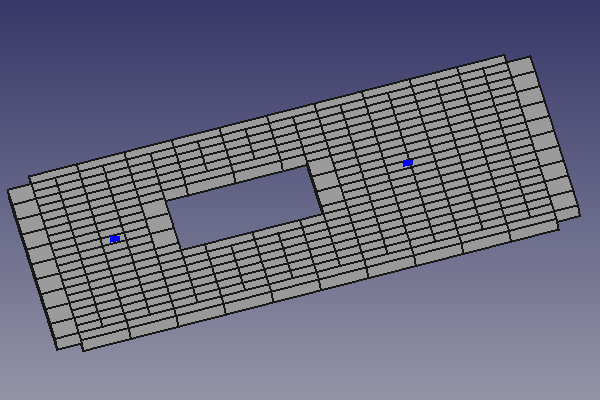
Das Werkzeug FHPlane fügt ein FastHenry-Objekt einer Ebene mit gleichförmiger Leitfähigkeit ein.
FastHenry FHEbene
Anwendung
Das FHPlane-Objekt muss auf einem anderen Objekt basieren, das entweder ein Draft Rechteck oder ein Part Quader-Objekt sein kann. Wenn das FHPlane-Objekt auf einem Part Quader-Objekt basiert, wird der Parameter Thickness vom Wert Box Height übernommen.
- Ein
Draft Rechteck oder ein
Part Quader-Objekt erstellen und auswählen
- Die Schaltfläche
EM FHPlane drücken, oder die Tasten E dann P drücken.
Darüber hinaus kann zusammen mit dem Basisobjekt (dem Draft Rechteck oder dem Part Quader) auch ein oder mehrere EM FHKnoten und/oder ein oder mehrere EM FHEbenenLoch-Objekte ausgewählt werden, die von FHEbene übernommen werden:
- Ein Draft Rechteck- oder ein Part Quader-Objekt erstellen
- Ein oder mehrere
EM FHNode-Objekte erstellen
- Ein oder mehrere
EM FHPlaneHole-Objekte erstellen
- Das Basisobjekt, die FHNode-Objekte und die FHPlaneHole-Objekte auswählen (für diese Mehrfachauswahl können die Objekte in der Baumansicht oder in der 3D-Ansicht angeklickt werden und zur Mehrfachauswahl einfach die STRG-Taste während der Auswahl gedrückt halten).
- Die Taste
EM FHPlane drücken oder die Tasten E und dann P drücken.
Anmerkungen
Ein FastHenry-Objekt mit gleichmäßiger Leitfähigkeit wird gebildet, indem ein Gitter aus Knoten (im Folgenden als 'interne Knoten' bezeichnet) angelegt und die Knoten mit einem 2D-Netz aus Segmenten in (relativer) X- und Y-Richtung verbunden werden. Löcher werden in der Ebene gebildet, indem einige interne Knoten und damit auch die Segmente, die mit diesen Knoten verbunden sind, entfernt werden. Weitere Informationen zu FastHenry-einheitlichen leitfähigen Ebenen findet man im FastHenry-Benutzerhandbuch.
- Da das FHPlane-Objekt auf einem Entwurfsrechteck- oder Teilekastenobjekt basiert, kann man die FHEbene NICHT frei verschieben. Die FHEbene ist immer an das Basisobjekt gebunden. Um die Position der FHEbene zu ändern, wendet man die Änderung auf das zugrunde liegende Basisobjekt an (das Basisobjekt ist standardmäßig ausgeblendet, man kann es wieder einblenden, indem man das Objekt in der Baumstruktur auswählt und die Leertaste drückt. Der Ursprung der FHEbene ist der Ursprung des Basisobjekts.
- Wenn die FHNode-Objekte von der FHEbene übernommen werden, werden ihre (X, Y, Z)-Koordinaten relativ zum Ursprung der FHEbene festgelegt (d. h., während die FHKnoten ihre Position im Raum beibehält, werden die relativen Koordinaten (X, Y, Z) der FHKnoten so geändert, dass sie relativ zum Ursprung der FHEbene sind). Außerdem wird die Z-Koordinate des FHKnoten nach der Übernahme auf Null zurückgesetzt (da die Koordinaten relativ zur FHEbene sind, entspricht die Z-Koordinate der Höhe des Objekts über der Ebene). Aus diesem Grund ist der Knoten nur von der Unterseite der FHEbene aus sichtbar, oder indem man die Transparenz der FHEbene ändert, um die FHKnoten durchzusehen, oder indem man die FHEbene ganz ausblendet. Um zu zeigen, dass der FHKnoten nun zur FHEbene gehört, wird außerdem die Farbe des FHKnotens geändert.
- Wenn die FHPlaneHole-Objekte von der FHEbene übernommen werden, werden ihre (X, Y, Z)-Koordinaten relativ zum Ursprung der FHEbene festgelegt (d. h., während das FHPlaneHole die gleiche Position im Raum beibehält, werden die relativen Koordinaten (X, Y, Z) des FHPlaneHole so geändert, dass sie relativ zum Ursprung der FHEbene sind). Außerdem wird die Z-Koordinate des FHPlaneHole nach der Übernahme auf Null zurückgesetzt (da die Koordinaten relativ zur FHEbene sind, ist die Z-Koordinate die Höhe des Objekts vom FHEbene aus). Aus diesem Grund ist der Knoten nur von der Unterseite der FHPlane aus sichtbar, oder indem man die Transparenz der FHEbene ändert, um die FHKnoten durchzusehen, oder indem man die FHEbene ganz ausblendet. Um zu zeigen, dass der FHKnoten nun zur FHEbene gehört, wird außerdem die Farbe des FHKnotens geändert.
- Wenn man die FHKnoten oder die FHEbeneLöcher später aus der FHEbene entfernen möchte, kann der Befehl EM FHEbeneHinzufügenEntfernenKnotenLoch verwendet werden.
Eigenschaften
- Daten-EigenschaftBase: Das Basisobjekt, auf dem diese Komponente aufgebaut ist (ein Draft Rechteck oder ein Part Quader)
- Daten-EigenschaftThickness: Die Dicke der FHEbene (Parameter 'thick' in FastHenry). Wenn die FHEbene auf einem Part Quader basiert, wird dieser Wert vom Parameter Part Box Height übernommen.
- Daten-Eigenschaftseg1: Die Anzahl der Segmente entlang der Längsrichtung (Parameter 'seg1' in FastHenry)
- Daten-Eigenschaftseg2: Die Anzahl der Segmente entlang der Breitenrichtung (Parameter 'seg2' in FastHenry)
- Daten-Eigenschaftnhinc: Die Anzahl der Filamente Die Ebenendicke (Ebenenparameter 'nhinc' in FastHenry)
- Daten-Eigenschaftrh: Das Verhältnis benachbarter Filamente entlang der Dicke (Parameter 'rh' in FastHenry)
- Daten-EigenschaftSigma: Die FHPlane-Leitfähigkeit (Parameter 'Sigma' in FastHenry)
- Daten-Eigenschaftsegwid1: Die Breite der Segmente entlang der Längsrichtung der Ebene (Ebenenparameter 'segwid1' in FastHenry)
- Daten-Eigenschaftsegwid2: die Breite der Segmente entlang der Ebenenbreitenrichtung (Ebenenparameter 'segwid2' in FastHenry)
- Daten-EigenschaftNodes: Die Liste der FHNode-Objekte für Verbindungen zum Flugzeug
- Daten-EigenschaftHoles: Die Liste der FHEbeneLöcher in der Ebene
- Daten-EigenschaftFineMesh: Gibt an, ob dieses feine Netz der Ebene angezeigt wird (d. h. Segmente zusammensetzt)
- Daten-EigenschaftShowNodes: Zeige das interne Knotennetz, das die Ebene stützt (d. h. interne Knoten).
Skripten
Siehe auch: Grundlagen der Skripterstellung in FreeCAD.
Das Objekt FHPlane kann in Makros und von der Python-Konsole aus mit der folgenden Funktion verwendet werden:
plane = makeFHPlane(baseobj=None, thickness=None, seg1=None, seg2=None, nodes=[], holes=[], name='FHPlane')
- Erstellt ein
FHPlane-Objekt. baseobjist das Draft Rechteck-Objekt oder Part Quader-Objekt, das als Basis für die FHEbene verwendet werden kann. Wenn keinbaseobjangegeben ist, muss der Benutzer später ein Basisobjekt zuweisen, um dieses Objekt verwenden zu können.thicknessist die Dicke der Ebene. Wennbaseobjein Part Box-Objekt ist, wird dieser Parameter ignoriert und stattdessen die Höhe des Part Box-Objekts verwendet. Der Standardwert istEMFHPLANE_DEF_THICKNESS.seg1ist eine Ganzzahl, die die Anzahl der Segmente entlang der x-Dimension der Ebene definiert (Parameter 'seg1' in FastHenry).seg2ist eine Ganzzahl, die die Anzahl der Segmente entlang der y-Dimension der Ebene definiert (Parameter 'seg2' in FastHenry).nodesist ein Array von FHNode-Objekten, das die Knoten angibt, die von der Ebene übernommen werden.holesist eine Anordnung von FHPlaneHole-Objekten, das die Löcher angibt, die von der Ebene übernommen werden.nameist der Name des Objekts.
Beispiel:
import FreeCAD, Draft, EM
pl = FreeCAD.Placement()
pl.Rotation.Q = (0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0)
pl.Base = FreeCAD.Vector(1.0,1.0,0.0)
rec = Draft.makeRectangle(length=10.0,height=5.0,placement=pl,face=True,support=None)
fhnode1 = EM.makeFHNode(X=1.0,Y=3.5,Z=0)
fhnode2 = EM.makeFHNode(X=8.0,Y=3.5,Z=0)
hole = EM.makeFHPlaneHole(X=6.0,Y=3.5,Z=0.0)
fhplane = EM.makeFHPlane(rect, thickness=1.0, seg1=15, seg2=15, nodes=[fhnode1, fhnode2], holes=[hole])
- FastHenry tools: FHNode, FHSegment, FHPath, FHPlane, FHPlaneHole, FHPlaneAddRemoveNodeHole, FHEquiv, FHPort, FHSolver, FHInputFile
- FasterCap tools: see GitHub source code
- Erste Schritte
- Installation: Herunterladen, Windows, Linux, Mac, Zusätzliche Komponenten, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Grundlagen: Über FreeCAD, Graphische Oberfläche, Mausbedienung, Auswahlmethoden, Objektname, Voreinstellungseditor, Arbeitsbereiche, Dokumentstruktur, Objekteigenschaften, FreeCAD unterstützen, Spenden
- Hilfe: Anleitungen, Videoanleitungen
- Arbeitsbereiche: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework