Macro TechDraw AuxiliaryView/de
Diese Seite beschreibt einen Anwendungsfall und enthält ein Makro, das eine Möglichkeit darstellt, eine Hilfsansicht zu erstellen.
Hoffentlich ist dies eine Anregung für einen C++ Programmierer, um diesen Machbarkeitsnachweis in einen integrierten TechDraw-Befehl zu überführen.
| Beschreibung |
|---|
| Dieses Makro fügt einem TechDraw-Zeichnungsblatt eine Hilfsansicht (auxiliary view) hinzu Versionsmakro : 0.02 Datum der letzten Änderung : 2025-06-27 Autor: FBXL5 |
| Autor |
| FBXL5 |
| Herunterladen |
| Links |
| Makros Rezepte Wie man Makros installiert Symbolleisten anpassen |
| Macro-Version |
| 0.02 |
| Datum der letzten Änderung |
| 2025-06-27 |
| FreeCAD-Version(s) |
| Standardverknüpfung |
| None |
| Siehe auch |
Einleitung
Nicht jeder, der eine Zeichnung mit seinem Modell mitliefern muss, kommt mit nur drei Hauptansichten (primären Ansichten) und Schnittansichten parallel zu diesen aus. Um ein Modell aus allen möglichen Winkeln abzubilden, sind Konstrukteure auf Hilfsansichten (auxiliary views, sekundäre Ansichten) angewiesen, die in einer bestimmten Anordnung auf einem Zeichenblatt positioniert werden, um den Weg nachverfolgen zu können, wie jede der verketteten Ansichten festgelegt wurde. Unzusammenhängende Ansichten, im 3D-Raum festgelegt und beliebig auf dem Zeichenblatt positioniert, sind kein brauchbarer Ersatz für richtig angeordnete Hilfsansichten.
Bis jetzt stellt diese Seite nur ein Makro bereit, das einen Machbarkeitsnachweis darstellt, der zeigt, dass es möglich ist, eine Hilfsansicht innerhalb einer Basisansicht festzulegen, ohne den Umweg über den 3D-Raum zu nehmen.
Beschreibung
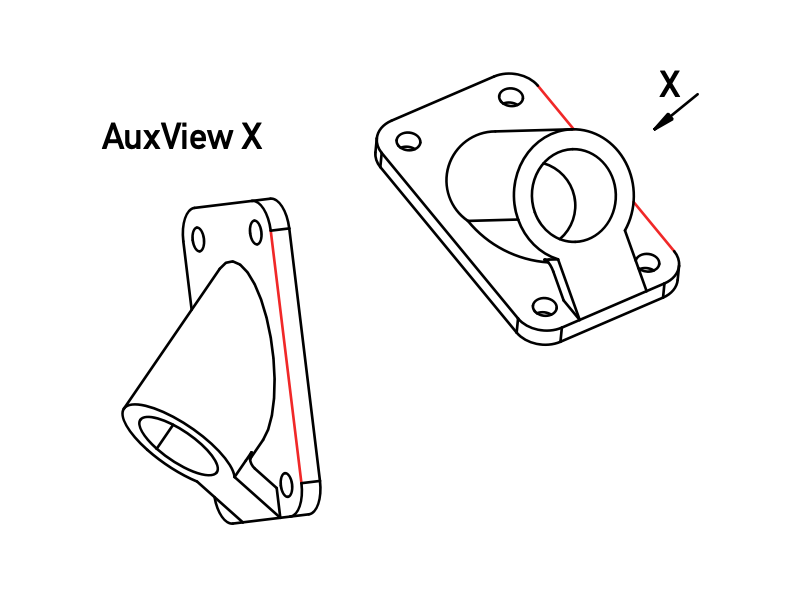
Das Macro TechDraw AuxiliaryView fügt einem TechDraw-Zeichnungsblatt eine Hilfsansicht (AuxView-Objekt) hinzu. Dies ist eine einfache Ansicht, die in einer Basisansicht festgelegt wird, anstatt im 3D-Raum.
Eine Hilfsansicht, die durch die rote Linie in der Basisansicht auf der rechten Seite bestimmt wird
Beispielanwendung
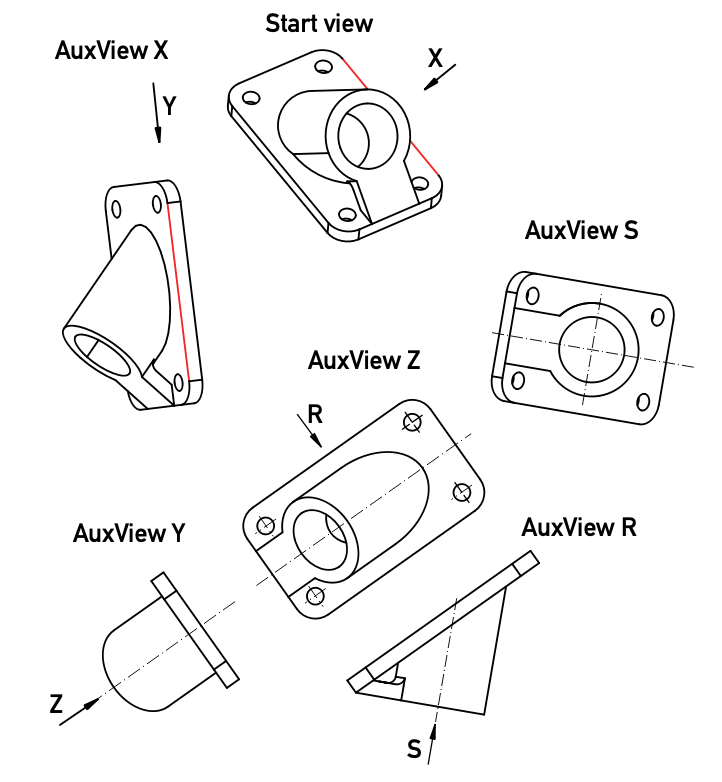
Gehen wir davon aus, dass uns eine netzparallele Ansicht vorliegt, aus der wir andere Ansichten ableiten wollen, um die wahren Formen der Formelemente darzustellen, die bemaßt werden sollen.
Die Schlüsselidee ist, eine gerade Linie in der Basisansicht auszuwählen, und senkrecht darauf eine Hilfsansicht festzulegen; diese ist die Basisansicht für eine weitere Hilfsansicht entlang der geraden Linie. Wir können Hilfsansichten aneinanderketten, bis wir alle drei Hauptansichten des Objekts und eine entlang der zylindrischen Teilform erstellt haben:
Die beliebig positionierte gerade Linie (rot) in der Ausgangsansicht (Start view) wird in der Hilfsansicht X (AuxView X) als Linie mit wahrer Länge und in der Hilfsansicht Y als Punkt projiziert, wo wir auch die wahre Breite und die wahre Stärke der Bodenplatte erkennen. Hilfsansicht Z wird senkrecht zur Bodenplatte festgelegt und stellt die wahre Form der Bodenplatte und ihrer Löcher dar. Hilfsansicht R steht senkrecht auf der längeren Kante der Bodenplatte und zeigt die wahren Winkel von Boden- und Deckelfläche der zylindrischen Teilform und wie sie zur Bodenplatte passt. Die letzte, Hilfsansicht S, wird entlang der Zylinderachse festgelegt und zeigt den Durchmesser und die Wandstärke der zylindrischen Teilform.
Das manuelle Zeichnen von Hilfsansichten erfordert eine zweite Basisansicht, um auf die Höhen über der Ebene der Basisansicht zuzugreifen, aber da FreeCAD die ganze Projektionsarbeit übernimmt, können wir uns allein auf die Richtung der Ansicht (Blickrichtung) konzentrieren.
Anwendung
- Sicherstellen, dass
Ansichtsrahmen eingeschaltet und Knotenpunkte auswählbar sind.
- Zwei Knotenpunkte in derselben Ansicht auswählen.
- Dieses Makro ausführen.
- Eine neue Hilfsansicht AuxView wird erstellt, einschließlich einer Kennzeichnung der Ansicht mit "AuxView X" (ein einfaches Textfeld).
- Ein Ansichtspfeil wird der Basisansicht hinzugefügt, einschließlich einer Kennzeichnung der Richtung mit "X".
- Die Hilfsansicht auf die gewünschte Position ziehen.
- Die Kennzeichnung der Richtung bearbeiten und die Kennzeichnung der Ansicht entsprechend anpassen.
Hinweise
- Die Auswahlreihenfolge der Knotenpunkte bestimmt die Ausrichtung der Ansicht.
- Der Ursprung der Ansicht ist der Mittelpunkt des Begrenzungsrahmens und daher nutzlos für geometrische Funktionen, wie das Messen des Abstandes zur Linie bzw. zum Vektor zwischen den ausgewählten Knotenpunkten. So ein Abstand würde das Festlegen einer Schnittlinie in der Basisansicht ermöglichen, und diese Information könnte im 3D-Raum zum Festlegen einer Schnittansicht verwendet werden.
- Die Hilfsansichten werden in der Mitte des Zeichnungsblattes erstellt und müssen manuell positioniert werden.
Ausklappen, um das Makro zu kopieren und einzufügen
Die Schaltfläche Makros... drücken und ein neues Makro erstellen. Das folgende Makro kopieren und in den Makro-Editor einfügen.
#! python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
This script creates an Auxiliary View from two selectec vertices
of one base view.
What is required: an active document, a drawing page containing one
or more views with a projection of a shape.
A possible workflow:
1. Extract base view from selection (two vertices)
2. Extract work page from app objects
3. Add a new view
4. Link base view from selection to new view
5. Link base view source to new view source
6. Retrieve new view's x direction from base view's x direction
7. calculate new view's z direction from new view's x direction
and base view's z direction
8. Set new view rotation including base view rotation
9. (Add annotations etc.)
I have tried to follow this naming rule:
class names: CamelCase
function names: mixedCase
constant names: ALL_CAPITAL + underscore
variable names: lower_case + underscore
"""
__Name__= ""
__Comment__ = ""
__Author__ = "FBXL5"
__Version__ = "00.02"
__Date__ = "2025-06-27"
__License__ = "LGPL-2.0-or-later"
__Web__ = ""
__Wiki__ = ""
__Icon__ = ""
__IconW__ = ""
__Help__ = ""
__Status__ = "Alpha"
__Requires__ = "FreeCAD >= 1.0 + Python3"
__Communication__ = "https://www.freecad.org/wiki/index.php?title=User: FBXL5"
__Files__ = ""
import math # to use some predefined conversions
from PySide.QtGui import (QMessageBox)
ARROW = """<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<svg
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1"
width ="16.8mm"
height="2.8mm"
viewBox=" 0 -1.4 16.8 2.8">
<g id="ArrowHead"
style="fill:#000;fill-opacity:1;stroke:#000;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:round;stroke-linejoin:round;font-size:5.0;text-anchor:middle;font-family:osifont">
<path d="m 0.3 0.0 h 16 " />
<path d="m 0.3 0.0 l 8.0 1.05 v -2.1 z " />
</g>
</svg>
"""
def displayMessage(title,message):
'''
displayMessage('Title','Messagetext')
'''
message_box = QMessageBox()
message_box.setText(message)
message_box.setWindowTitle(title)
message_box.exec()
def getActiveDocument():
'''
Returns the active document or sends a message
'''
ado = App.activeDocument()
if ado is not None:
return ado
displayMessage("AuxView", "No active document available!")
return False
# (borrowed from TechDraw sources)
def getSelView(nSel=0):
'''
view = getSelView()
nSel=0 ... number of selected view, 0 = first selected
Return selected view, otherwise return False
'''
if not Gui.Selection.getSelection():
view = None
displayMessage('AuxView','No view selected')
else:
view = Gui.Selection.getSelection()[nSel]
return view
# (borrowed from TechDraw sources)
def getSelVertexes(nVertex=1, nSel=0):
'''
vertexes = getSelVertexes(nVertex)
nVertex=1 ... min. number of selected vertexes
nSel=0 ... number of selected view, 0 = first selected
Return a list of selected vertexes if at least nVertex vertexes are selected, otherwise return False
'''
if getSelView(nSel):
view = getSelView(nSel)
else:
return False
if not Gui.Selection.getSelectionEx():
displayMessage('AuxView','No vertex selected')
return False
objectList = Gui.Selection.getSelectionEx()[nSel].SubElementNames
vertexes = []
for objectString in objectList:
if objectString[0:6] == 'Vertex':
vertexes.append(view.getVertexBySelection(objectString))
if (len(vertexes) < nVertex):
displayMessage('AuxView','Select at least '+
str(nVertex)+' vertices')
return False
else:
return vertexes
def getPageOfSelection(doc, b_view):
'''Retrieves the Page that holds the selected elements'''
#- Find an object starting with 'Page' that contains the selected object
for each in doc.Objects:
if each.Name.startswith("Page"): # [0:4] == 'Page':
for item in each.OutList: # Search items belonging to a Page object
if item.Name.startswith("ProjGroup"): # Look into projection groups
for view in item.OutList: # Search views belonging to a ProjGroup object
if view.Name == b_view.Name:
return each
else:
if item.Name == b_view.Name:
return each
return False
def getCcwAngle(vertex1,vertex2,view_rotation):
'''Creates 3D vectors to calculate the 2D angle towards the x direction of the
base view which is parallel to the page view's x direction.
The direction of the XDirection property is not parallel to the view's
x direction if the view is rotated! This angle also has to be taken into
account to calculate the 3D angle'''
#- Extract position vectors from the points
vector_start = App.Vector(vertex1.X, vertex1.Y, vertex1.Z)
vector_end = App.Vector(vertex2.X, vertex2.Y, vertex2.Z)
#- Calculate the 2D Direction vector from start vertex to end vertex
# on the XY plane of the base view/work page (z = 0)
direction = vector_end.sub(vector_start)
x_direction = App.Vector(1, 0, 0)
angle_x = math.degrees(direction.getAngle(x_direction))
# getAngle() returns positive (absolute) values only (in rad)
# -> convert to degrees and check orientation
if vertex1.Y > vertex2.Y:
angle_x *= -1 # switches angle orientation
#- Turn back the base view rotation
# angle_x is a float value now but view_rotation is deg
#print('a. angle_x: ', angle_x)
#print('b. view_rotation: ', float(view_rotation))
angle_x -= float(view_rotation)
return angle_x
def symbolAngle(vertex1,vertex2):
'''
Creates 3D vectors to calculate the 2D angle towards the x direction of the
base view
'''
#- Extract position vectors from the points
vector_start = FreeCAD.Vector(vertex1.X, vertex1.Y, vertex1.Z)
vector_end = FreeCAD.Vector(vertex2.X, vertex2.Y, vertex2.Z)
#- Calculate the 2D Direction vector from start vertex to end vertex
# on the XY plane of the base view/work page (z = 0)
direction = vector_end.sub(vector_start)
y_direction = FreeCAD.Vector(0, -1, 0)
angle_y = math.degrees(direction.getAngle(y_direction))
# getAngle() returns positive (absolute) values only (in rad)
# -> convert to degrees and check orientation
if vertex1.X > vertex2.X:
angle_y *= -1 # switches angle orientation
return angle_y
def main():
''' The main section, no more, no less '''
# Operations are performed in the active document of the application
#- Retrieve the active document
active_doc = getActiveDocument()
if not active_doc: # (active_doc is None/False)
return
#- Retrieve the selection view and selected vertices
if getSelView() and getSelVertexes(2):
base_view = getSelView()
vertices = getSelVertexes(2) # required number of vertices
else:
return
#- Retrieve the page that holds the view
work_page = getPageOfSelection(active_doc, base_view)
if not work_page:
# this should always be true as selected vertices are already checked
return
# At this point the input elements are gathered:
# active_doc, work_page, base_view, and vertices
#- Create a new view
new_view = active_doc.addObject('TechDraw::DrawViewPart', 'AuxView')
#- Add the new view to the page
work_page.addView(new_view)
#- Add a BaseView property to the new view
new_view.addProperty('App::PropertyLink','BaseView')
#- Link the BaseView object to the BaseView property
new_view.BaseView = active_doc.getObject(base_view.Name)
#- Hand over the source objects
new_view.Source = new_view.BaseView.Source
#- 2D: Calculate the ccw angle between the x axes of base view and new view
turn_ccw = getCcwAngle(vertices[0],vertices[1],new_view.BaseView.Rotation)
# Returns a float value representing degrees
# 3D: Turn base_view.XDirection around base_view.Direction to get
# new_view.XDirection
#- Create a rotation, angle input in float (for degrees), stored in rad
around_direction = App.Rotation(new_view.BaseView.Direction, turn_ccw)
#- Apply rotation to the base_view.XDirection
new_view.XDirection = around_direction.multVec(new_view.BaseView.XDirection)
#- The cross-product of base view Z and new view X gives new view Z direction
new_view.Direction = new_view.BaseView.Direction.cross(new_view.XDirection)
# 2D: Take base_view.Rotation into account, it has to be converted
# to float since it is stored in deg
#- Add the rotation of the base view to the angle between the x axes
new_view.Rotation = turn_ccw + float(new_view.BaseView.Rotation)
Gui.runCommand('TechDraw_RedrawPage',0)
# At this point the Auxiliary View is complete
#- Create an arrow symbol
new_symbol = active_doc.addObject('TechDraw::DrawViewSymbol', 'Symbol')
new_symbol.Symbol = ARROW
new_symbol.Owner = base_view
new_symbol.Rotation = symbolAngle(vertices[0],vertices[1])
#- Add the new symbol to the page
work_page.addView(new_symbol)
#- Create a direction tag
dir_tag = active_doc.addObject('TechDraw::DrawViewAnnotation', 'DirTag')
dir_tag.Text = "X"
dir_tag.Owner = new_symbol
#- Add the new symbol to the page
work_page.addView(dir_tag)
#- Create a view tag
view_tag = active_doc.addObject('TechDraw::DrawViewAnnotation', 'ViewTag')
view_tag.Text = "AuxView X"
view_tag.Owner = new_view
#- Add the new symbol to the page
work_page.addView(view_tag)
FreeCADGui.runCommand("TechDraw_RedrawPage",0)
FreeCADGui.runCommand("TechDraw_RedrawPage",0)
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
# This will be true only if the file is "executed"
# but not if imported as module
main()
- Blätter (Seiten): Neues Zeichnungsblatt aus der Standardvorlage erstellen, Neues Zeichnungsblatt aus einer Vorlage erstellen, Seite neu zeichnen, Alle Seiten drucken
- Ansichten: Ansicht einfügen, Aktive (3D-)Ansicht einfügen, Ansichtengruppe einfügen, Schnittansicht einfügen, Komplexe Schnittansicht einfügen, Detailansicht einfügen, Objekt des Arbeitsbereichs Draft einfügen, Objekt des Arbeitsbereichs Arch einfügent, Tabellenansicht einfügen, Ausschnittsgruppe einfügen, Ansicht teilen, Form projizieren
- Stapeln: Ansicht auf die Stapeloberseite bewegen, Ansicht auf die Stapelunterseite bewegen, Ansicht um eine Ebene nach oben bewegen, Ansicht um eine Ebene nach unten bewegen
- Verzierungen: Fläche mit Muster aus einer Bilddatei schraffieren, Fläche mit einer geometrischen Schraffur versehen, SVG-Zeichnungselement einfügen, Bitmap-Grafik einfügen, Ansichtsrahmen ein- oder ausschalten
- Maßeinträge: Längenmaß einfügen, Horizontales Maß einfügen, Vertikales Maß einfügen, Radienmaß einfügen, Durchmessermaß einfügen, Winkelmaß einfügen, Winkelmaß über 3 Punkte einfügen, Maß für die horizontale Ausdehnung einfügen, Maß für die Vertikale Ausdehnung einfügen, Maß mit 3D-Geometrie verknüpfen, Hinweisfeld einfügen, Axonometrisches Längenmaß, Maß zwischen Orientierungspunkten einfügen, Maßreferenzen reparieren
- Anmerkungen: Anmerkung einfügen, Hinweislinie zur Ansicht hinzufügen, Rich-Text-Anmerkung einfügen, Hilfspunkt hinzufügen, Kantenmittelpunkte hinzufügen, Quadrantengrenzpunkte hinzufügen, Mittellinie zu Fläche(n) hinzufügen, Mittellinie zwischen 2 Linien hinzufügen, Mittellinie zwischen 2 Punkte hinzufügen, Hilfslinie durch 2 Punkte hinzufügen, Hilfskreis hinzufügen, Liniendarstellung ändern, Ausgeblendete Kanten ein-/ausblenden, Hinzufügen von Schweißinformationen zur Hinweislinie, Oberflächensymbol erstellen, Wellen- oder Bohrungspassung hinzufügen
- Ergänzungen:
- Merkmale und Änderungen: Linienmerkmale, Zeilenabstand und Längendifferenz auswählen, Linienmerkmale ändern, Linie verlängern, Linie kürzen, Ansicht fixieren/lösen, Schnittansicht ausrichten, Horizontale Kettenmaße anordnen, Vertikale Kettenmaße anordnen, Schräge Kettenmaße anordnen, Horizontale Maße anordnen, Vertikale Maße anordnen, Schräge Maße anordnen, Flächeninhalt der ausgewählten Flächen berechnen, Bogenlänge der ausgewählten Kanten berechnen, Formatierung anpassen
- Mittellinien und Gewinde: Kreismittellinien hinzufügen, Lochkreismittellinien hinzufügen, Hilfslinien für Innengewinde in Seitenansicht hinzufügen, Hilfslinien für Innengewinde in Achsansicht hinzufügen, Hilfslinien für Außengewinde in Seitenansicht hinzufügen, Hilfslinien für Außengewinde in Achsansicht hinzufügen, Hilfsschnittpunkte hinzufügen, Add an offset vertex, Hilfskreis hinzufügen, Hilfsbogen hinzufügen, Hilfskreis über 3 Punkte hinzufügen, Parallele Hilfslinie hinzufügen, Senkrechte Hilfslinie hinzufügen
- Maße: Horizontale Maßkette erstellen, Vertikale Maßkette erstellen, Schräge Maßketten erstellen, Horizontale Koordinatenmaße erstellen, Vertikale Koordinatenmaße erstellen, Schräge Koordinatenmaße erstellen, Horizontales Maß an Fase erstellen, Vertikales Maß an Fase erstellen, Bogenmaß erstellen, '⌀'-Symbol einfügen, '□'-Symbol einfügen, Präfixsymbol entfernen, Dezimalstellenanzahl erhöhen, Dezimalstellenanzahl verringern
- Exportieren: Seite als SVG-Datei exportieren, Seite als DXF-Datei exportieren
- Zusätzliche Funktionen: Liniengruppen, Vorlagen, Schraffieren, Form- und Lagetolerierung, Einstellungen
- Erste Schritte
- Installation: Herunterladen, Windows, Linux, Mac, Zusätzliche Komponenten, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Grundlagen: Über FreeCAD, Graphische Oberfläche, Mausbedienung, Auswahlmethoden, Objektname, Voreinstellungseditor, Arbeitsbereiche, Dokumentstruktur, Objekteigenschaften, FreeCAD unterstützen, Spenden
- Hilfe: Anleitungen, Videoanleitungen
- Arbeitsbereiche: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework