Arch Window
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| 3D/BIM → Window |
| Workbenches |
| BIM |
| Default shortcut |
| W I |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| None |
Description
The Arch Window tool creates a base object for all kinds of "embeddable" objects, such as windows and doors. It is designed to be either independent, or "hosted" inside another component such as an Arch Wall, Arch Structure, or Arch Roof. It has its own geometry, that can be made of several solid components (commonly a frame and inner panels), and also defines a volume to be subtracted from the host objects, in order to create an opening.
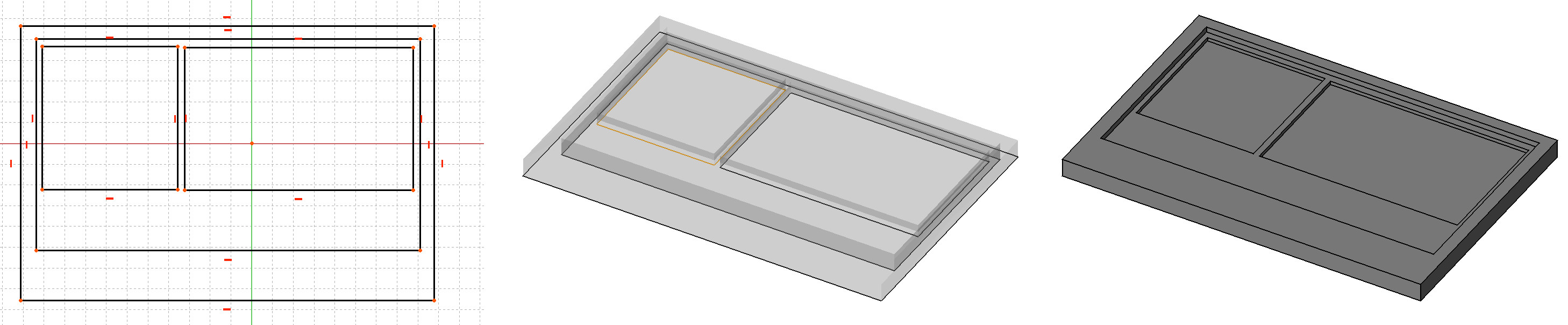
Window objects can be based on closed 2D objects, such as Draft Rectangles or Sketches, that are used to define their inner components. The base 2D object must therefore contain several closed wires, that can be combined to form filled panels (one wire) or frames (several wires).
The Window tool features several presets. These allow the user to create common types of windows and doors with certain editable parameters, without the need to create the base 2D objects and components manually.
All information applicable to an Arch Window also applies to an Arch Door, as it is the same underlying object.
Complex window being constructed on top of a Sketch. When entering the window's edit mode you can create different components, set their thickness, and select and assign wires from the sketch to them.
Usage
There are different ways to create windows, depending on the desired level of detail and functionality.
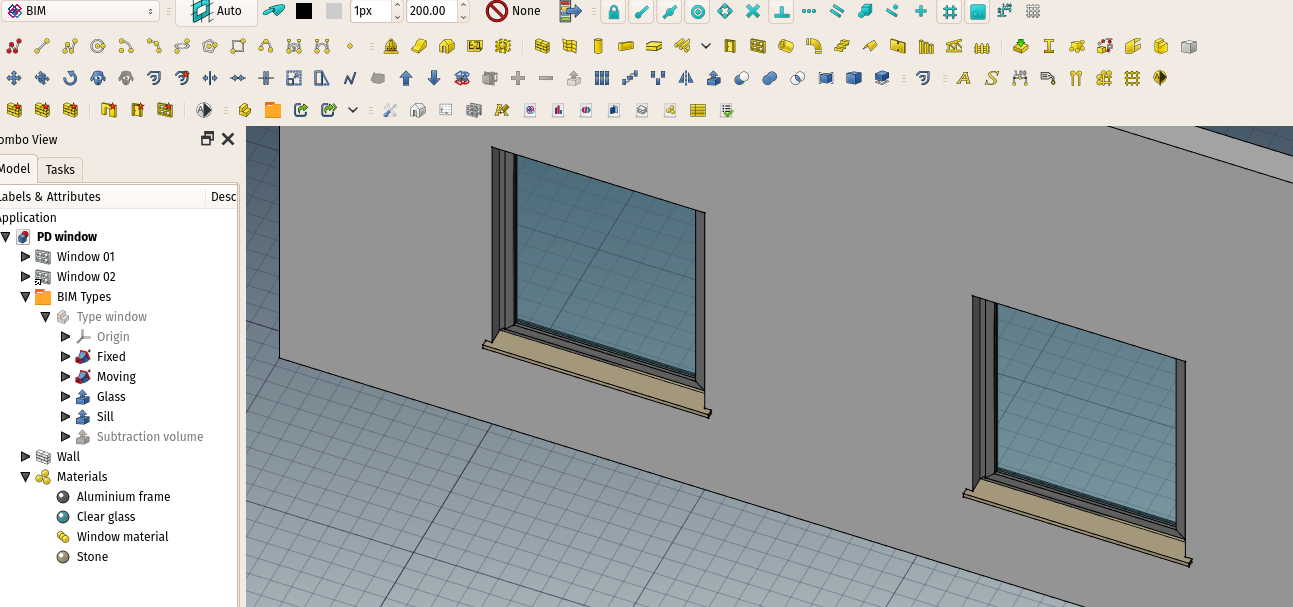
Creating a window from a preset
This is the most straightforward way of creation, where existing presets cover the most general types of windows.
- There are several ways to invoke the tool:
- Press the
Window button.
- Select the 3D/BIM →
Window option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: W then I.
- Press the
- Select one of the presets in the list.
- Fill out the desired parameters.
- In the 3D View, move the window to the location where you wish to place it. If you move the pointer over an Arch Wall, the outline of the window should align itself with the face of that object.
- Click on the 3D View with the mouse, or press the Enter key three times to confirm the X-, Y-, Z-coordinates of the placement.
Learn more about presets.
Creating a window from custom components
When the desired window format is not covered by any of the existing presets, custom windows can be created and optionally included as user presets in addition to the built-in presets.
- Optionally, select a face on the Arch object where you want the window to be included, and then set the working plane to it.
- Create a new sketch with the
New Sketch command on the current working plane.
- For proper placement, the bottom left hand corner of the window should be at the sketch origin.
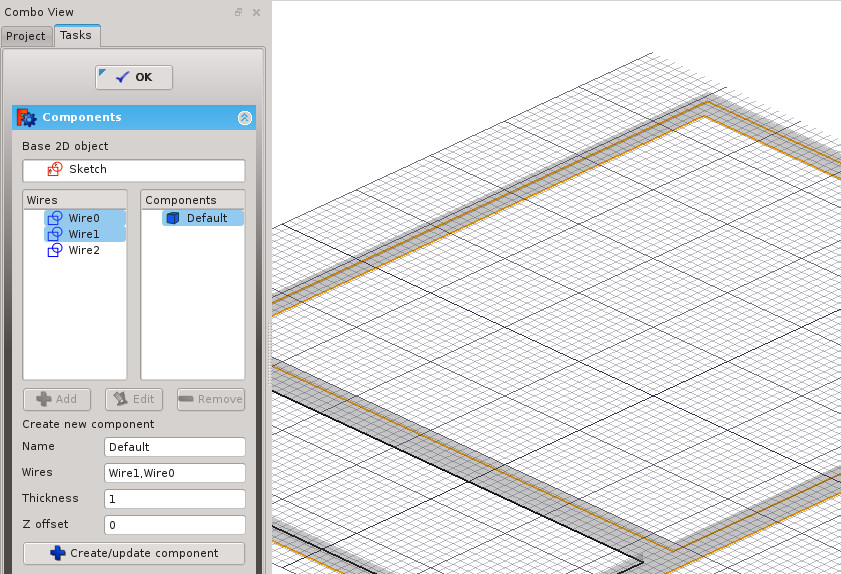
- Draw one or more closed wires (loops). Pay close attention to the creation order of these loops, the numbering of the "wires" in the task panel ("Window elements") depends on this.
- Close the sketch.
- Select the sketch and press the
Window button, or any of the alternative ways to invoke the tool.
- To adjust the window components and various properties, enter the window task panel by double-clicking on the created object in the Tree View.
- Note that since components following a hinged component will also hinge, all fixed components, such as outer frames and fixed glass panels, must be defined before any hinged components. And a glass panel in a hinged frame must be defined after that frame, and before any other hinged components.
Learn more about custom components.
Creating a window from custom types
- Create a window frame object, a glass panel, and any other window component you need, using Part Workbench or PartDesign tools.
- For example, create a base rectangular sketch for your window, then a profile sketch for the frame, and create a Part Sweep to sweep the profile around the base sketch. Create a Part Offset2D from the base sketch, then a Part Extrude to create the glass panel
- Optionally, create a volume to be subtracted from the wall, for example by extruding the base sketch.
- Make sure all these pieces have a unique, meaningful name (for example, "Frame" or "Glass panel")
- Create an App Part, and place all your subcomponents in it
- If you have created one, make sure the subtraction volume's visibility is turned off
- If you want to make your window parametric, you can add 3 properties to your App Part, by right-clicking its Property View and selecting "Add Property". Add the following properties (all of them are optional, the property group doesn't matter):
- Height as a PropertyLength and link it, for example, to a vertical constraint of your base sketch.
- Width as a PropertyLength and link it, for example, to a horizontal constraint of your base sketch.
- Subvolume as a PropertyLink and link it to the volume to be subtracted that we created above.
- Tag as a PropertyString.
- To create window objects from the newly-created type. select the App Part and press the
Window button, or any of the alternative ways to invoke the tool.
The DataHeight, DataWidth, DataSubvolume and DataTag properties of the window will be linked to the corresponding property of the App Part, if existing.
Learn more about custom types.
Strategies for placing windows
TBD - explain:
- Links vs clones - Advanced snapping
Options
- If the Auto include in host object checkbox on the Window creation task panel is unchecked, the window won't be inserted into any host object on creation.
- Add a selected window to a wall by selecting both, then pressing the
Add Component button. The order of selection is important: first select the window, then the wall.
- Remove a selected window from a wall by selecting the window, then pressing the
Remove Component button.
- When using presets, it is often convenient to turn the "Near" Draft Snap on, so you can snap your window to an existing face.
- The hole created by a window in its host object is determined by two properties: DataHole Depth and DataHole Wire. The Hole Wire number can be picked in the 3D View from the window's task panel available after double-clicking the window in the Tree View
- Windows can make use of Multi-Materials. The window will search in the attached Multi-Material for material layers with a same name for each of its window component, and use it if any is found. For example, a component named "OuterFrame" will search in the attached Multi-Material, for a material layer named "OuterFrame". If such material layer is found, its material will be attributed to the OuterFrame component. The thickness value of the material layer is disregarded.
Openings
See also: Tutorial for open windows
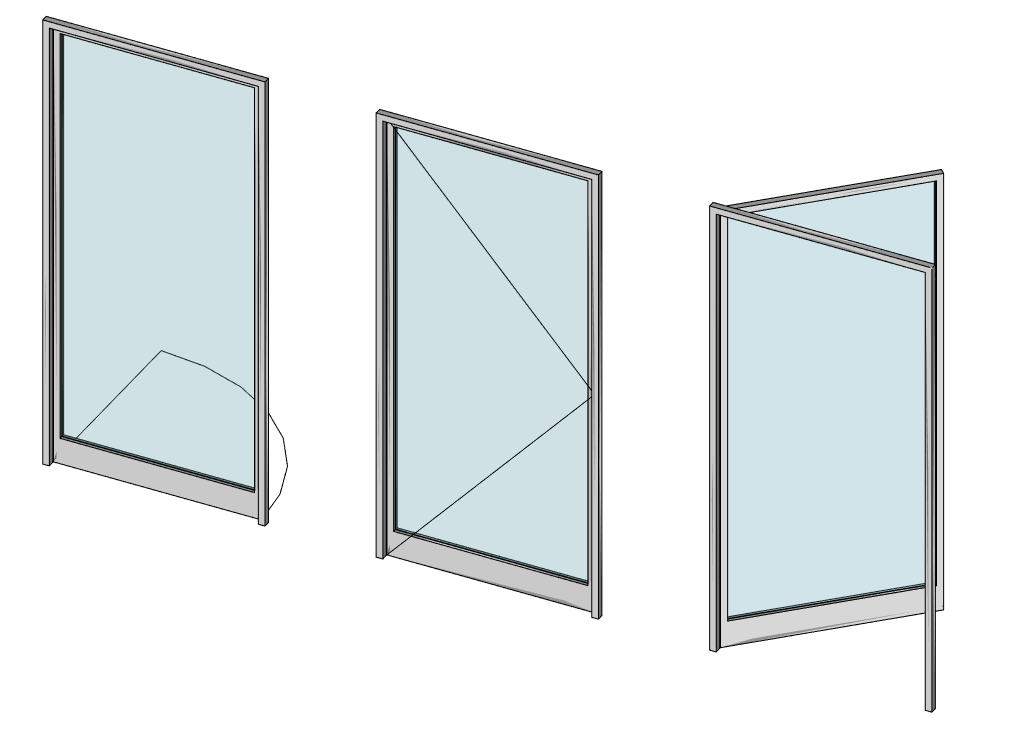
Doors and windows can appear partially or fully opened in the 3D model, or can display opening symbols both in plan and/or elevation. Consequently, these will also appear in extracted 2D views generated by Draft Shape2DView or the TechDraw Workbench. To obtain this, at least one of the window components must have a hinge and an opening mode defined (see Custom components). Then, using the DataOpening, DataSymbol Plan or DataSymbol Elevation properties, you can configure the appearance of the window:
A door showing the symbol plan, symbol elevation and opening properties at work
Presets
The following presets are available:
-
Fixed
-
Open 1-pane
-
Open 2-pane
-
Sash 2-pane
-
Sliding 2-pane
-
Simple door
-
Glass door
-
Sliding 4-pane
-
Awning
-
Opening only introduced in 1.0
Additional user presets
In addition to the default presets, the window tool can also use custom presets. A custom preset is a FreeCAD file containing a single window based on a parametric sketch that has two named constrains: Width and Height. Custom presets can be placed in the following locations:
$ROOT_DIR/Arch/Doors/Custom/
$ROOT_DIR/Arch/Windows/Custom/
If you install the Parts Library from the Addon Manager, the window tool will also search this library for additional presets at this pair of locations:
$ROOT_DIR/Mod/parts_library/Architectural Parts/Doors/Custom/
$ROOT_DIR/Mod/parts_library/Architectural Parts/Windows/Custom/
- The $ROOT_DIR is the user directory where FreeCAD configuration files, macros, and external workbenches are stored. It can be found be entering
FreeCAD.getUserAppDataDir()in the Python Console.- On Linux it is usually /home/username/.local/share/FreeCAD/
- On Windows it is usually C:\Users\username\Application Data\FreeCAD\
- On Mac OSX it is usually /Users/username/Library/Preferences/FreeCAD/
- The subdirectory name Custom is just a suggestion, any name can be used. But the files must be placed in one or more subdirectories inside the Doors or Windows directories.
Custom presets will be available in the window tool's presets dropdown menu. Presets in library locations will also be available in the Parts Library dialog.
Custom components
You can access, create, modify and delete components of a window in edit mode (double-click the window in the Tree View).
Windows can include 4 types of components: frames, solid panels, glass panels and louvres. Panels and louvres are made from one closed wire, which gets extruded, while frames are made from 2 or more closed wire, where each one is extruded, then the smaller ones are subtracted from the biggest one.
The components have the following properties:
- Name: A name for the component
- Type: The type of component. Can be "Frame", "Glass panel", "Solid panel" or "Louvres"
- Wires: A comma-separated list of wires the component is based on
- Thickness: The extrusion thickness of the component
- Z Offset: The distance between the component and its base 2D wire(s)
- Hinge: This allows you to select an edge from the base 2D object, then set that edge as a hinge for this component and the next ones in the list
- Opening mode: If you defined a hinge in this component or any other earlier in the list, setting the opening mode will allow the window to appear open or to display 2D opening symbols in plan or elevation.
Custom types
Windows can also take advantage of other tools, specifically PartDesign workflows, to define a type. A type is an object that defines the shape of the window. This is specially well suited to work with Std Parts:
Download the example file shown above
Note that windows created in this manner do not support the Openings features.
Materials
To build a material for type-based windows:
- Create a multi-material.
- Create one entry in the multi-material for each component of your Std Part. For example, one "Frame", one "Glass panel" as we used above. Make sure to use the exact same name.
- Attribute that multi-material to each of the windows derived from the same type.
You can use any other kind of workflow than the one described above, the important points to remember are:
- The type object must be one object, no matter the type (Std Part or PartDesign Body).
- The type object must have a "Subvolume" property (linked to the window's Subvolume property) for openings in host objects to work.
- The type object must have a "Group" property with different children with same names as multi-material items for multi-materials to work.
Properties
An Arch Window object shares the common properties and behaviors of all Arch Components.
Data
Window
- DataArea (
Area): The area of this window. - DataFrame (
Length): The frame size (thickness/depth) of this window. - DataHeight (
Length): The height of this window. - DataHole Depth (
Length): The depth of the hole created by this window in its host object. - DataHole Wire (
Integer): The number of the wire from the base object that is used to create a hole in the host object of this window. This value can be set graphically when double-clicking the window in the Tree View. Setting a value of 0 will make the window automatically pick its biggest wire for the hole. - DataHosts (
LinkList): The objects (e.g. wall) that host this window. - DataLouvre Spacing (
Length): If any of the components is set to "Louvres", this property defines the spacing between the louvre elements. - DataLouvre Width (
Length): If any of the components is set to "Louvres", this property defines the size of the louvre elements. - DataNormal (
Vector): The normal direction of this window, set (hardcoded) by the Window tool at interactive mode. Remarks: Set to (0,0,0) to make window automatically deduce the Normal direction, useful when user rotate the window's base Sketch e.g. when its host wall is rotated. - DataOffset (
Length): The offset size (from base sketch) of this window. - DataOpening (
Percent): All components that have their opening mode set, and provided a hinge is defined in them or in an earlier component in the list, will appear open by a percentage defined by this value. - Data (Hidden)Preset (
Integer): The preset number this window is based on. - DataSubvolume (
Link): An optional object that defines a volume to be subtracted from hosts of this window. - DataSymbol Elevation (
Bool): Shows 2D opening symbol in elevation. - DataSymbol Plan (
Bool): Shows 2D opening symbol in plan. - DataWidth (
Length): The width of this window. - Data (Hidden)Window Parts (
StringList): The components of this window (5 strings per component).
Scripting
See also: Arch API and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
The Window tool can be used in macros and from the Python console by using the following function:
Window = makeWindow(baseobj=None, width=None, height=None, parts=None, name="Window")
- Creates a
Windowobject based onbaseobj, which should be a well formed, closed Draft Wire or Sketcher Sketch. - If available, sets the
width,height, andname(label) of the Window. - If the
baseobjis not a closed shape, the tool may not create a proper solid figure.
Example:
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
import Arch
rect = Draft.makeRectangle(length=900, height=3000)
# Optional: rotate it to be on the XZ plane, so that the window is upright
rect.Placement.Rotation = App.Rotation(App.Vector(1, 0, 0), 90)
App.ActiveDocument.recompute()
Window = Arch.makeWindow(rect)
App.ActiveDocument.recompute()
You can also create a Window from a preset.
Window = makeWindowPreset(windowtype, width, height, h1, h2, h3, w1, w2, o1, o2, placement=None)
- Creates a
Windowobject based onwindowtype, which should be one of the names defined inArch.WindowPresets. widthandheightdefine the total size of the object, with units in millimeters.- The parameters
h1,h2,h3(vertical offsets),w1,w2(widths),o1, ando2(horizontal offsets) specify different distances in millimeters, and depend on the type of preset being created. - If a
placementis given, it is used.
Example:
import FreeCAD as App
import Arch
base = App.Vector(2000, 0, 0)
axis = App.Vector(1, 0, 0)
place= App.Placement(base, App.Rotation(axis, 90))
door = Arch.makeWindowPreset("Simple door",
width=900, height=2000,
h1=100, h2=100, h3=100, w1=200, w2=100, o1=0, o2=100,
placement=place)
- 2D drafting: Sketch, Line, Polyline, Circle, Arc, Arc From 3 Points, Fillet, Ellipse, Polygon, Rectangle, B-Spline, Bézier Curve, Cubic Bézier Curve, Point
- 3D/BIM: Project, Site, Building, Level, Space, Wall, Curtain Wall, Column, Beam, Slab, Door, Window, Pipe, Connector, Stairs, Roof, Panel, Frame, Fence, Truss, Equipment
- Reinforcement Tools: Custom Rebar, Straight Rebar, U-Shape Rebar, L-Shape Rebar, Stirrup, Bent-Shape Rebar, Helical Rebar, Column Reinforcement, Beam Reinforcement, Slab Reinforcement, Footing Reinforcement
- Generic 3D Tools: Profile, Box, Shape Builder, Facebinder, Objects Library, Component, External Reference
- Annotation: Text, Shape From Text, Aligned Dimension, Horizontal Dimension, Vertical Dimension, Leader, Label, Hatch, Axis, Axis System, Grid, Section Plane, New Page, New View
- Create 2D Views: 2D Drawing, Section View, Section Cut
- Snapping: Snap Lock, Snap Endpoint, Snap Midpoint, Snap Center, Snap Angle, Snap Intersection, Snap Perpendicular, Snap Extension, Snap Parallel, Snap Special, Snap Near, Snap Ortho, Snap Grid, Snap Working Plane, Snap Dimensions, Toggle Grid, Working Plane Front, Working Plane Top, Working Plane Side, Working Plane
- Modify: Move, Copy, Rotate, Clone, Create Simple Copy, Create Compound, Offset, 2D Offset, Trimex, Join, Split, Scale, Stretch, Draft to Sketch, Upgrade, Downgrade, Add Component, Remove Component, Array, Path Array, Polar Array, Point Array, Cut With Plane, Mirror, Extrude, Difference, Union, Intersection
- Manage: BIM Setup, Views Manager, Setup Project, Manage Doors and Windows, Manage IFC Elements, Manage IFC Quantities, Manage IFC Properties, Manage Classification, Manage Layers, Material, Schedule, Preflight Checks, Annotation Styles
- Utils: Toggle Bottom Panels, Move to Trash, Working Plane View, Select Group, Set Slope, Working Plane Proxy, Add to Construction Group, Split Mesh, Mesh to Shape, Select Non-Manifold Meshes, Remove Shape From BIM, Close Holes, Merge Walls, Check, Toggle IFC B-Rep Flag, Toggle Subcomponents, Survey, IFC Diff, IFC Explorer, New IFC Spreadsheet, Image Plane, Unclone, Rewire, Glue, Re-Extrude
- Panel Tools: Panel, Panel Cut, Panel Sheet, Nest
- Structure Tools: Structure, Structural System, Multiple Structures
- IFC Tools: IFC Diff, IFC Expand, Create IFC Project, IfcOpenShell Update
- Nudge: Nudge Switch, Nudge Up, Nudge Down, Nudge Left, Nudge Right, Nudge Rotate Left, Nudge Rotate Right, Nudge Extend, Nudge Shrink
- Additional: Preferences, Fine tuning, Import Export Preferences, IFC, DAE, OBJ, JSON, 3DS, SHP
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub